Sense, solve, go: Does Waymo herald the future of autonomous vehicles?
By Scott Simmie
During a recent trip to California, I had the opportunity to ride in a Waymo.
I’d certainly read about Alphabet’s autonomous car-for-hire service in the past and work for a company that builds robots and autonomy software. So it seemed a natural, while in San Francisco, to download the app (similar to Uber) and hail an autonomous vehicle.
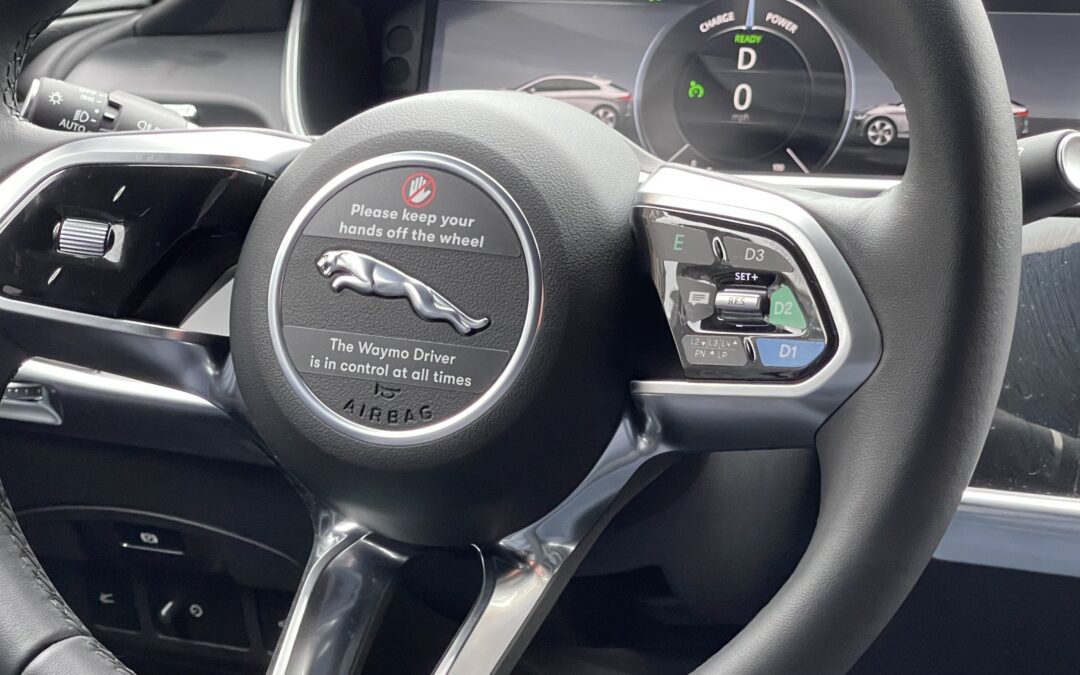
Within a couple of minutes, a Waymo vehicle arrived at the pickup point – just a short walk from where it had been summoned. It pulled up, LiDARs spinning, waiting for me to climb in. I put a hand on the door; it was locked. A quick glance at the app and I saw an “unlock” feature. Then I was inside.
And then, with some ambient music playing in the background (you have the option to turn it off or select something else), we – meaning the car and I – were off. A display showed a digital representation of what the vehicle was seeing in its surroundings, including parked vehicles and pedestrians. The electric Jaguar quietly accelerated to the speed limit, obeyed all traffic rules, and smoothly adjusted for unexpected occurrences. When the driver of a parked vehicle opened the door to exit, the Waymo liquidly arced a safe distance away. With the steering wheel making smooth turns and constant smaller fine adjustments, it was like being in a vehicle with an invisible, silent driver at the helm.
I had full faith in the technology and actually preferred it to a standard rideshare. Waymo’s safety data (which we’ll explore later) had reassured me the drive was going to be statistically safer than riding with a human driver. Plus, there was no need to engage in small talk. When the ride was done, I simply exited without being prompted for a tip.
I’d been aware of Waymo since it first deployed. I also have a friend with a Tesla who has the Full Self-Driving package. He commutes twice a week from well outside Toronto into the GTA without any inputs beyond setting his destination. He foresees a day, long promised by Elon Musk, when his own vehicle will earn him money by working during off hours as an autonomous taxi.
The technology for fully autonomous vehicles is basically here – arriving both sooner and later than some had predicted. But what does that mean for the future?
Below: A Waymo Driver waits patiently at an intersection – while another Waymo Driver glides past. Photos by Scott Simmie

SENSE, SOLVE, GO
Owned by Google parent company Alphabet, Waymo states “We’re on a mission to be the world’s most trusted driver. Making it safer, more accessible, and more sustainable to get around — without the need for anyone in the driver’s seat.” It calls its service, the app and the car together, Waymo One. The system, the hardware and software, are referred to collectively as Waymo Driver.
Commercial rollout began in Phoenix, Arizona in 2020, with testing in San Francisco commencing late the following year. It’s now also operating in Los Angeles, with expansion into Atlanta, Austin and Miami next. It uses a Jaguar I-PACE electric vehicle as its base, heavily outfitted with an array of sensors. We’re talking a lot of sensors.
In total there are 29 cameras, six radar and five LiDAR units (including a roof-mounted 360° LiDAR). These sensors allow Waymo Driver to fully capture its environment up to three football fields away. Powerful AI, machine vision and machine learning software continuously crunch predictive algorithms allowing Waymo to understand where a pedestrian, cyclist or other vehicle will most likely continue based on current trajectory. And, of course, if one of those moving subjects suddenly does something unexpected/unpredicted, the system quickly readjusts. Waymo touts safety stats (which we’ll explore later) it says proves Waymo Driver is far safer than a human driver.
Waymo boils down the entire process to three words: Sense, solve, go. Waymo Driver senses its environment using the sensors mentioned above (it also has an array of External Audio Receivers – EARs – which alert the system if they detect sirens, etc. It can even echolocate the location of said sirens and will understand if it needs to pull over). The algorithms solve the challenge of safely moving through that environment, including moving objects, and then it’s go time. Those three simple words represent a decade and a half of intense R&D, development of its own sensors, and a huge capital expenditure.
Google first began exploring self-driving vehicles in earnest back in January of 2009. By the time it revealed this publicly, it had already done extensive R&D and testing. But it wasn’t until the fall of 2015 that the first solo member of the public climbed into a Waymo in Austin, Texas and took the vehicle for a ride on city streets. That passenger was Steve Mahan, who is legally blind. It was the first time in 12 years that he’d been alone in a car. It would be another five years before the first rollout to the public.
During that five years, both the car and sensor package – along with the software – evolved considerably. Just compare videos below; the first shows Steve Mahan on that historic trip in 2015, the second is an updated video explaining the fifth-generation Waymo Driver.
SAFETY FIRST
Waymo could pitch its offering on a number of grounds: Sustainability, convenience, cool factor. But instead, it focuses its customer-facing marketing on safety. Waymo Driver, it says repeatedly, is far safer than a human driver. It has proven that in many millions of miles on the streets, it says, and billions more in simulation.
The statistics Waymo publishes are based on Incidents Per Million Miles (IPMM) of driving – and compare its own rates of incidents with a benchmark of IPMM involving human drivers. Whether it’s airbag deployments, crashes with a reported injury, or incidents where police are notified, Waymo’s stats are consistently a fraction of those involving people at the wheel. In more than 33 million miles of driving, Waymo touts these as the results:
- 81 per cent fewer airbag deployment crashes
- 78 per cent fewer injury-causing crashes
- 62 per cent fewer police-reported crashes
That’s clearly a significant reduction, and to most people would indicate that Waymo is safer than taking a ride with a stranger (or even friend) at the wheel. The statistics include accidents where other drivers were at fault, but does not separate them out – so we can’t actually see what percentage involved an error from the Waymo side. Waymo has previously stated that the majority of these incidents were the fault of human drivers, and that there have been but two accidents involving injuries where it expects to pay out insurance liability claims.
But even rare incidents can quickly become high-profile. In Phoenix, an empty Waymo that had been summoned by a customer crashed at low speed into a telephone pole in an alley. Had a human been at the wheel, we would never have heard of it. But because it was a Waymo, the incident led newscasts. Why is that? Well, we expect perfection in systems like these. And that seems a reasonable expectation if you’re going to trust your personal safety to a driverless car. It just can’t make mistakes. And that’s why Waymo quickly issued a recall for a software fix.
“This is our second voluntary recall,” Katherine Barna, a Waymo spokesperson, told TechCrunch. “This reflects how seriously we take our responsibility to safely deploy our technology and to transparently communicate with the public.”
In May of 2024, the US National Highway Transportation Safety Agency (NHTSA) informed Waymo it was investigating 22 incidents involving its vehicles (and subsequently added an additional nine incidents), stretching back to 2001. Many of those incidents were described by Forbes as “surprisingly minor” and 11 of those incidents were culled by the NHTSA from social media reports of the vehicles driving in an unusual fashion (such as using the oncoming lane to avoid traffic problems). The most serious was the aforementioned pole collision.
We were unable to find any reports of Waymo incidents involving a serious injury. The one fatality involving a Waymo occurred in January of 2025, when an unoccupied stationary Waymo stopped at a traffic light was one of several vehicles hit by a speeding car. One person and a dog died in that incident, but because a Waymo was tangentially involved it made the headlines. It is the only case we can find involving a fully driverless vehicle where a fatality was involved – and in this case the vehicle was completely passive. (There was a pedestrian fatality in 2018 involving an autonomous Uber vehicle. In that incident, which occurred in Tempe, Arizona, a human safety driver was in the driver’s seat. She was watching television on her phone when the accident occurred and subsequently pleaded guilty to endangerment.)
While Waymo has an excellent track record, there have been incidents. But with each incident where Waymo Driver has somehow made the wrong decision, it’s reasonable to assume it was followed by a software fix. And here’s where a fleet of autonomous vehicles have a definite advantage over people: That tweak can be instantly applied to the entire fleet.
Still, there are skeptics who argue that – despite those millions of miles of driverless passenger trips – Waymo does not have enough data upon which to draw sound conclusions.
“We don’t know a lot. We know what Waymo tells us,” Philip Koopman, an expert on autonomous vehicle safety at Carnegie Mellon University, told the Miami Herald. “Basically you are trusting Waymo to do the right thing.”
THE FUTURE
Autonomy is hard – and it takes time: Google and Alphabet have invested more than 15 years of continuous engineering for Waymo Driver to reach this level of technological maturity.
Now, Waymo is rolling out to more cities. Remember those 672 Jaguars that had the software upgrade? They’re just a fraction of the 20,000 I-Pace vehicles Waymo signed a contract with Jaguar to purchase. Plus, the company recently announced that its six-generation vehicle – a Chinese-made electric minivan – is next up for testing and deployment. From all external appearances, Waymo shows no sign of stopping (except at red lights, of course). In 2024, it carried out four million autonomous rides – four times more than its total of trips over the previous four years. Rides in 2024 tripled to 150,000 per week. And the company calculates “Waymo riders helped avoid over 6 million kilograms of CO2 emissions.”
That’s all great. But for any commercial enterprise, even if it’s willing to absorb costs during rollout, the ultimate test will be the bottom line. Will Waymo prove profitable?
We can’t say for certain – and Waymo’s current financials are somewhat invisible to the public, as they’re bundled in with several other projects Alphabet projects. But some analysts predict Waymo, the clear leader in autonomous rideshare, will ultimately win a significant piece of the market. An analysis on Nasdaq.com predicts Waymo could prove over time to be the jewel in Alphabet’s crown.
“Uber does more than 200 million rides each week,” states the story. “Let’s let that sink in. So if autonomous rides can capture even half that market, that would mean 100 million rides per week…If Waymo can capture about one-third of the $1 trillion autonomous rides market, it could generate annual revenues of around $300 billion.” Enough, suggests the story, to double Alphabet’s stock price.
That’s a big prize. And, clearly, incentive for Alphabet and Waymo to continue on the road to profitability.
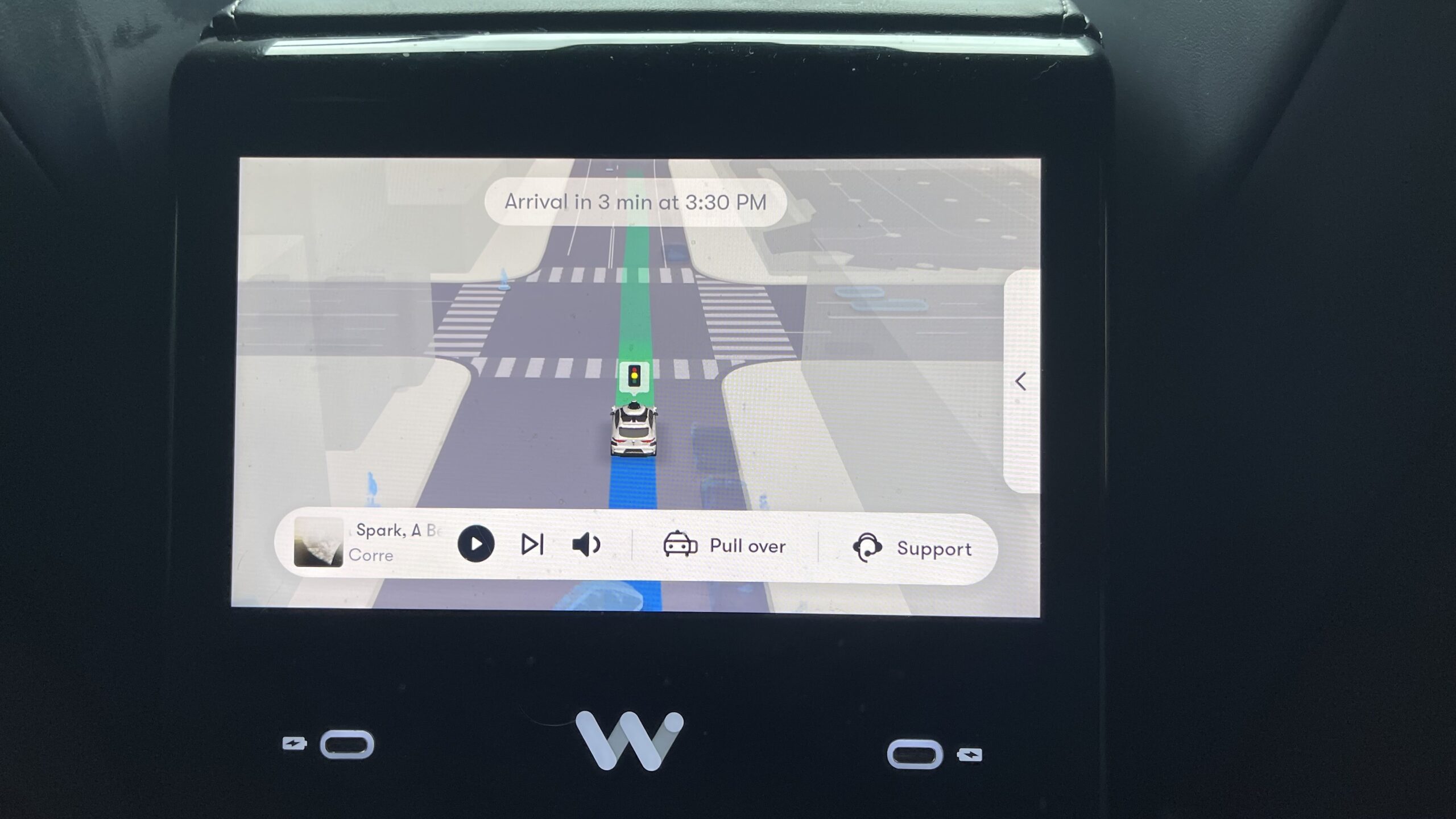
Below: The LCD display for rear Waymo passengers. Note the option to “pull over” if you unexpectedly need to end your ride early
INDRO’S TAKE
Because we’re deeply involved in the autonomous space, we obviously take great interest in Waymo and other deployments of autonomous technologies at scale. Waymo Driver is different from most other applications, though, because it’s transporting human beings. There is very little – if any – room for error.
“We can’t predict the future, but – like algorithms – can make informed predictions with available data,” observes InDro Robotics Founder and CEO Philip Reece. “Waymo appears to be heavily invested in continuously making a good safety record even better – and has the engineering and financial resources to do so. I suspect Waymo, and its competitors, are here to stay.”
For more on Waymo, check out its website. And, if you’re in one of the growing number of cities where it operates, download the app and let Waymo Driver take the wheel.