Assistive devices on the rise at Korea’s Robot World Conference
A major robotics conference is underway in Seoul, South Korea.
Robot World 2023 features some 200 exhibitors and 700 booths, ranging all the way from heavy hitters like Hyundai (which makes robots for industrial purposes) through to companies that manufacture the various widgets that make up the robot supply chain. There are manufacturers of wheels, servos, end effectors, lubricants, cable management systems – you name it, you’ll find it.
Need a hand? There’s no shortage of robotic arms. While many are suited for factory and warehouse work, others are destined for the food services industry. Turn a corner and you’re more likely than not to see an arm smoothly pouring a coffee, grabbing a soft drink or snack and presenting it to an attendee.
Below: A Hyundai robot that can lift and reposition autonomobiles. It’s part of the Hyundai WIA (World Industrial Ace) division.
USE-CASES
The robots at this show illustrate the many use-cases. There are welding robots, pick-and-place machines, and heavy-lift AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) that can lift more than a ton. Need something stacked, sorted, inspected, delivered? Want a manipulator arm you can program to start preparing French fries the moment a take-out order has been placed by an app? Need a robot to move a car?
At Robot World 2023, you’ll find all of the above – and more.
ASSISTIVE DEVICES
But there was another category of robot on display at the exhibition: Assistive medical devices. Specifically, very smart machines that can be used for patients requiring rehabilitation.
InDro Robotics, which was invited to attend Robot World 2023, was struck by the number of companies with products in this sector. There were ground robots – friendly-looking devices that keep an eye on vulnerable people and can call for assistance if there’s a fall or some other crisis. But more intriguing to us were machines that can play a role – both physiologically and psychologically – in helping to rehabilitate someone from a serious injury or other challenging condition.
Below: A shape-shifting wheelchair wheel can climb stairs

RE-LEARNING TO WALK
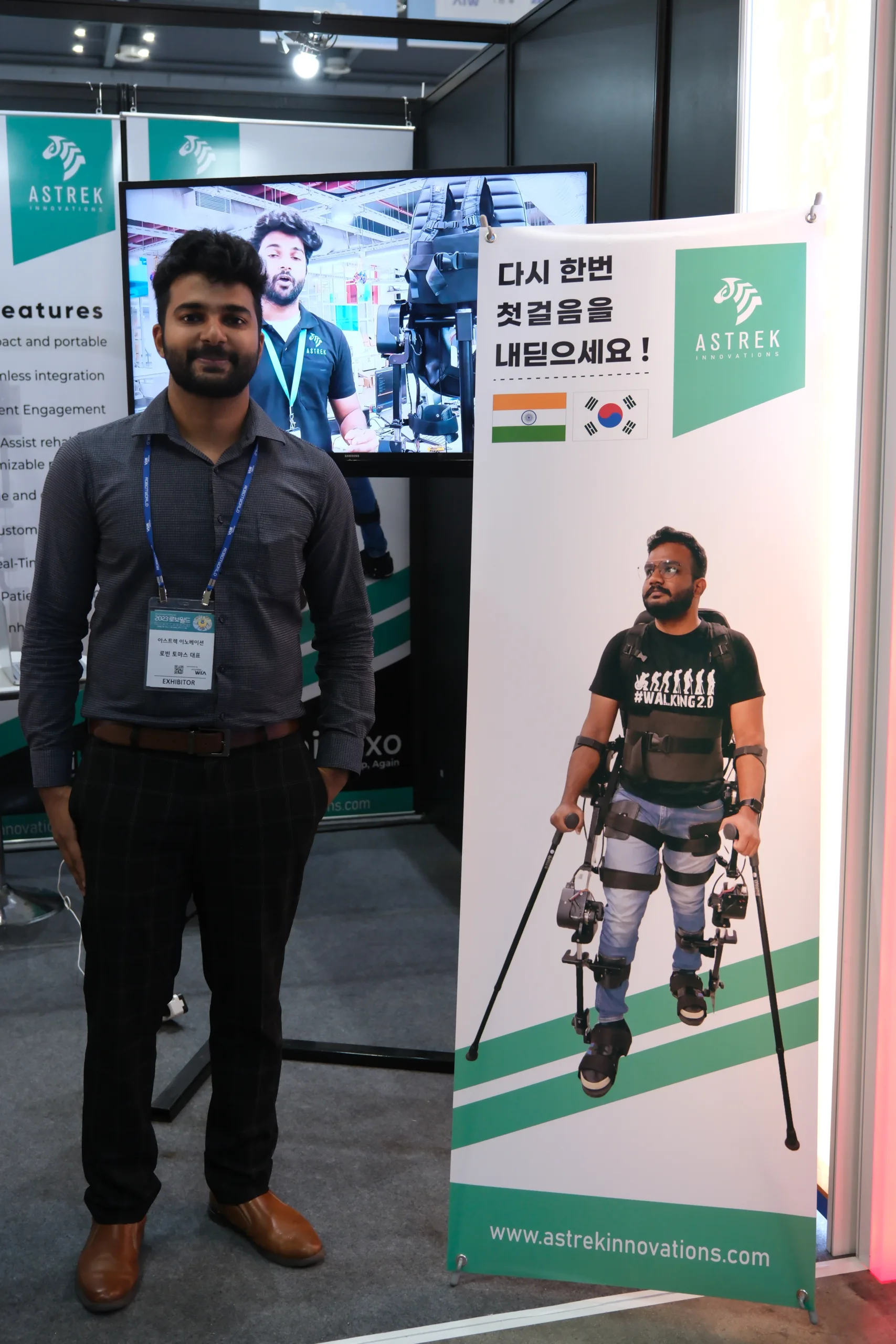
Like any major convention, exhibitors range from established global companies like Hyundai all the way to smaller startups with a great idea. And one that caught our attention is a company called Astrek Innovations. Its CEO and co-Founder is Robin Kanattu, a young engineer from Kerala in southern India.
“We are mainly focussing on building and designing products for the 20 per cent of people who are suffering from disability and accessibility issues,” says Robin. “One of the products is the lower limb exoskeleton, for people who are suffering form lower limb disabilities.”
As the company’s website explains:
“Established in 2018, we develop cutting edge solutions to some of our most complex problems – Disability and Rehabilitation. Leveraging our knowledge and expertise in robotics, machine learning and motion capture, we design devices that would transform the current state-of-the-art in the rehabilitation and assistive technology arena.
“Our magnum opus is a wearable robotic device, an exoskeleton, that would help people with lower-limb immobility walk again. A culmination of motorised limb braces, motion capturing & tracking; and machine learning; this device would transform rehabilitation into a precise, immediate treatment protocol.”
Established in 2018, the company has been building and testing versions of this product for four years.
“Now we have a final version, and we wanted to provide independence for people who are suffering form these disabilities,” he says.
A lot of research has gone into this product. Robin says a great deal of groundwork was spent capturing data on healthy people: How they walk, how they sit, how gaits alter during the course of a stride.
“Now we use that same data to predict the walking pattern of users, so they will have much more stable walking and standing while using the device.”
The exoskeleton provides support and strength and moves the legs. Forward-facing crutches are used to aid in stability. The product can be used on someone who is paralysed from the waist down, people recovering from strokes, those with certain genetic issues and people recovering from accidents.
HOW THE IDEA WAS BORN
Robin is an electrical engineer. But there was a personal motivation to put his skills to use in this arena.
“My grandfather had this issue. After having an accident, he was not able to walk properly. And after doing knee replacement surgery he was not able to walk again,” he explains. “So that’s how our team came togeher.”
Astrek has been recognized for product excellence at Robot World 2023, and Korea has brought the company in on a program called the K Startup Grand Challenge. Robin has been working in Korea on streamlining the manufacturing chain, working with mentors and looking for collaboration.
But the product, he says, is fully functioning. And people who are paralyzed from the waist down have been able to walk with it.
“Psychologically, they are so happy,” he says. “Their sole dream is to walk again, and we are happy to see them doing that.”
Robin did not have the prototype at the show because of red tape involving flying the batteries to Seoul. He’s pictured below with a banner showing the device.

ROBOT REHABILITATION
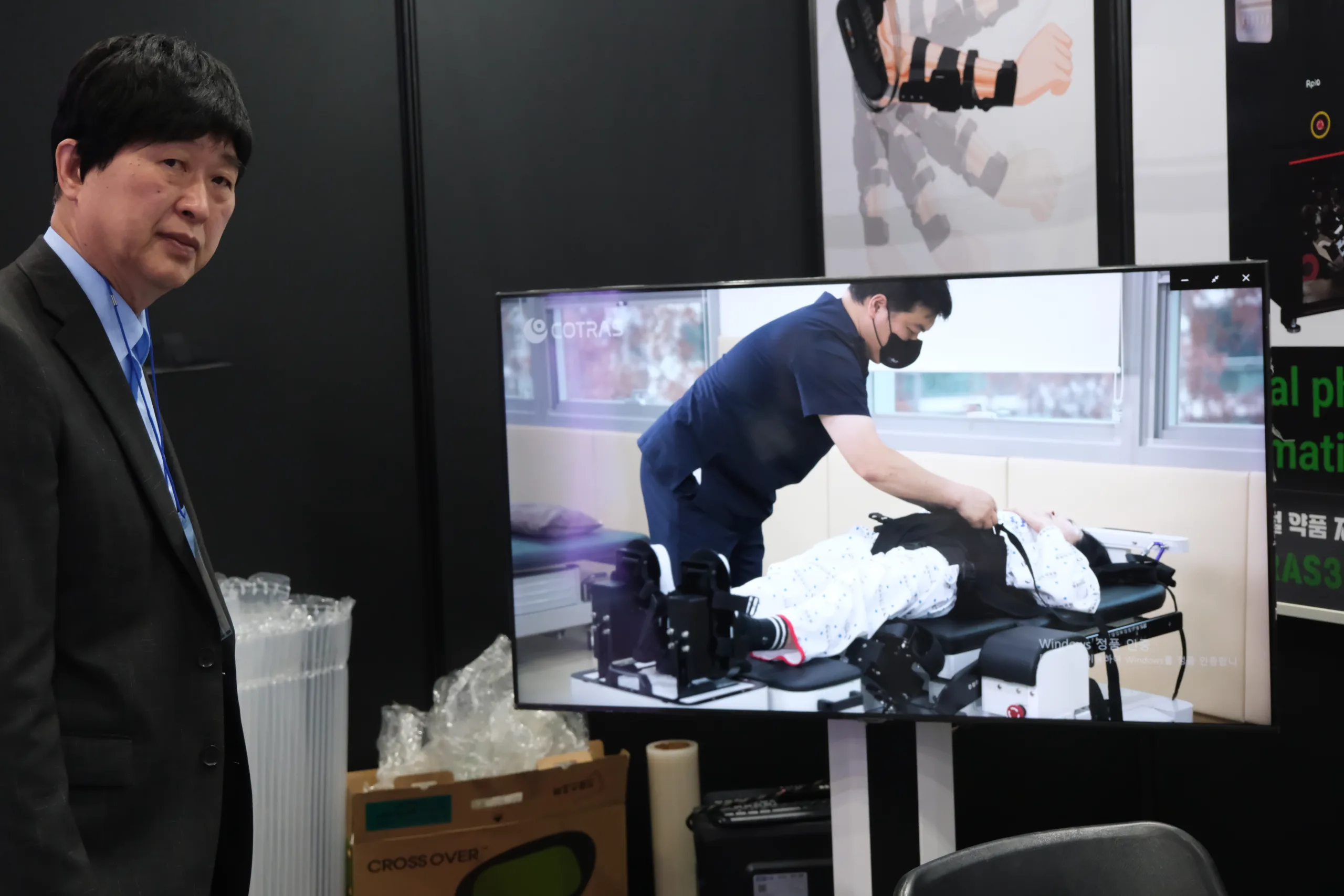
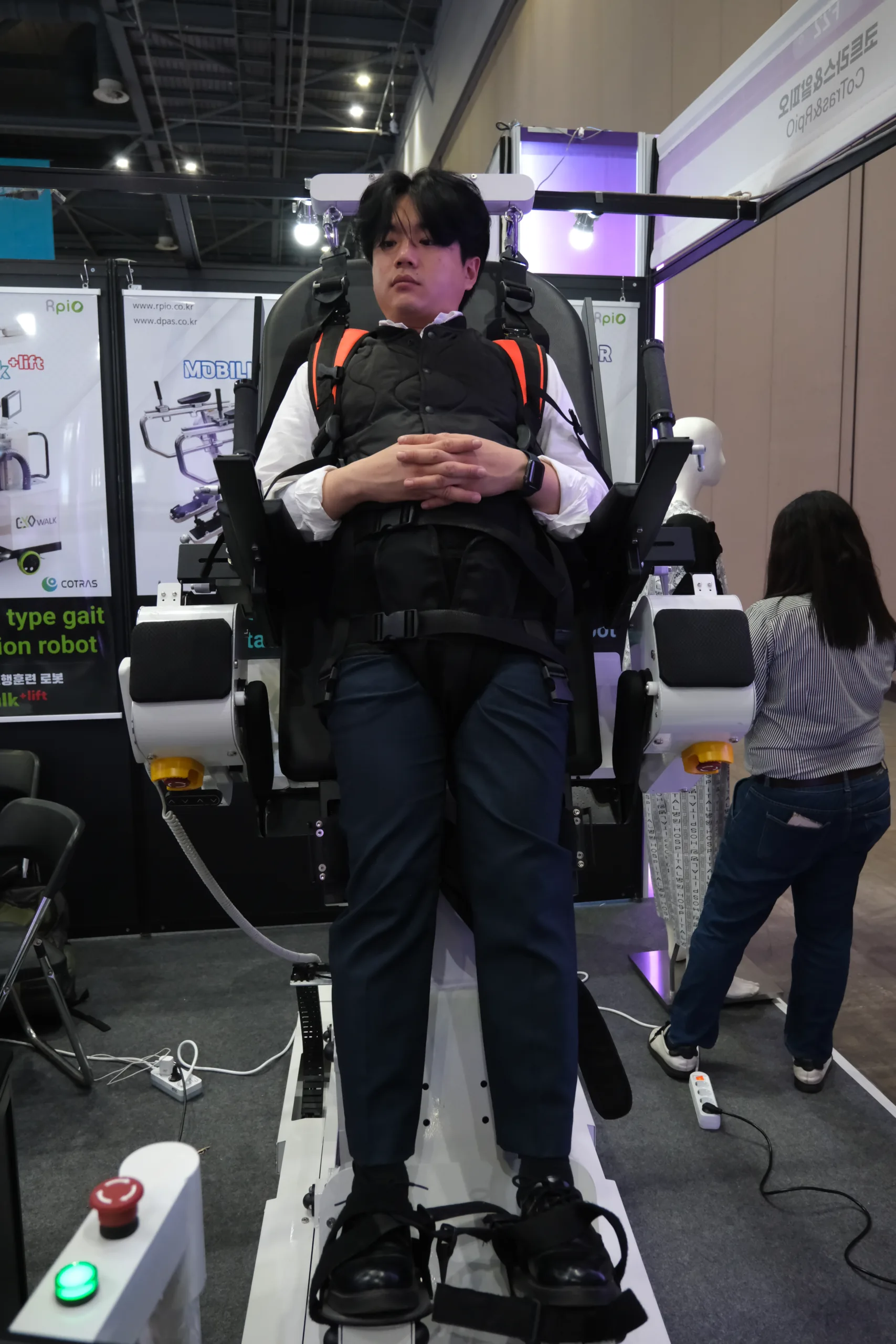
Another company, RpiO, has already cracked the market. Its R-BoT plus is a device designed for people with central nervous system damage (including stroke, paraplegia, spinal cord injury etc.). It’s more of a rehab device designed for hospital settings, but allows users to exercise lower extremities while lying down or standing upright. The product is approved by a Korean regulatory body (Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safey, formerly the KFDA), and the company has already sold seven units inside Korea.
“We have major hospitals, locals hospitals and private hospitals who are using the machine with people who have damage impacting their lower body,” explains CEO Jay Moh.
“Because KFDA is a standard in Southeast Asia, we are starting to sell in Hong Kong, Malaysia and Singapore. Many doctors have come to see our robots.”
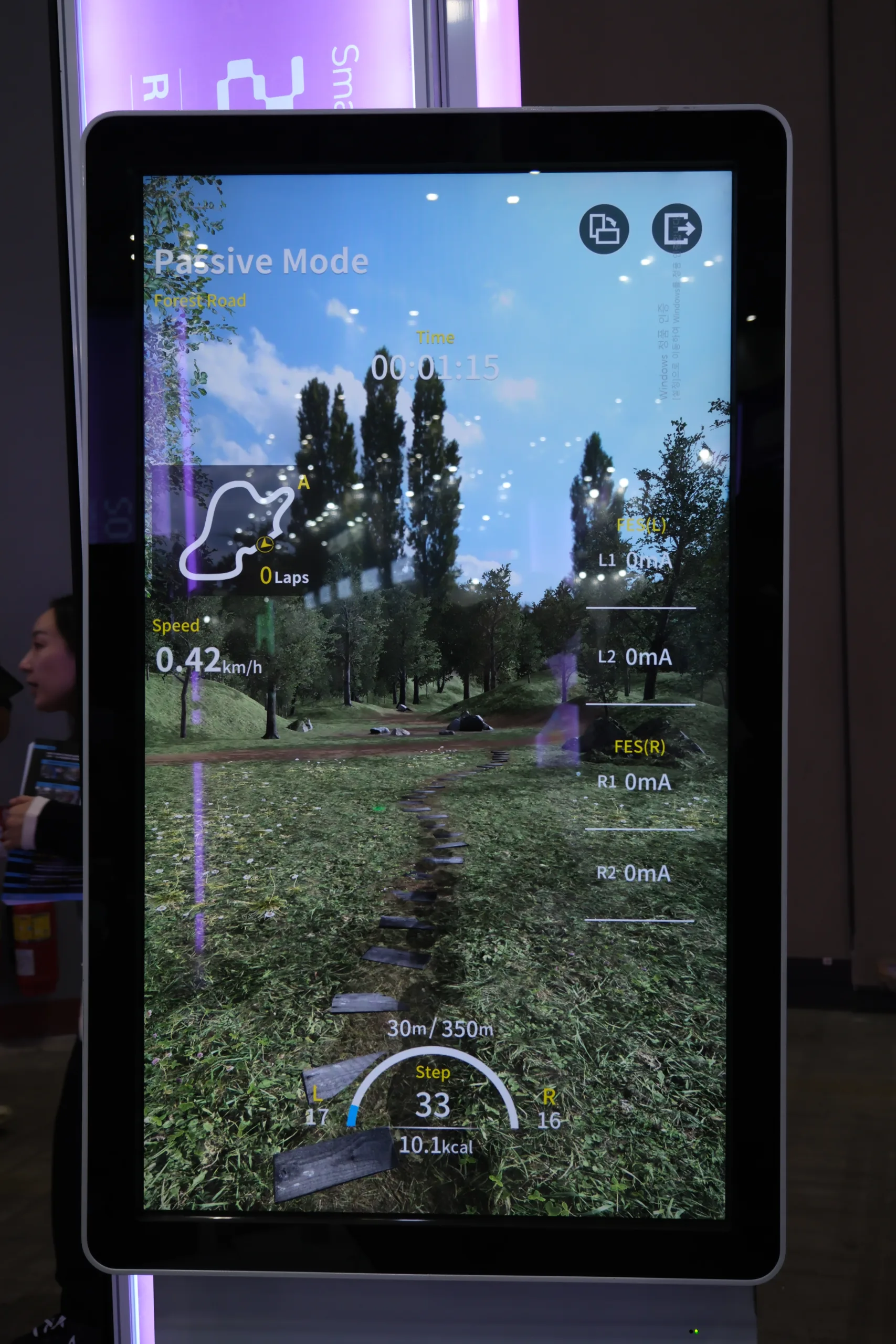
The R-BoT plus works in three modes: Passive, active and resistive – depending on the patient’s abilities. What sets this device apart is that the person exercising watches a large-screen display during rehabilitation sessions. The display features outdoor scenes, and with every ‘step’ made, a footprint appears on the ground and the patient has a visual cue that they’re making progress. Distance covered, calories burned and heart rate are all displayed as well, providing further incentive.
“Once the machine starts, they look at the display,” he says. “This has been medically tested; this stimulates the brain and releases a chemical that stimulates recovery. People feel better – they enjoy the workout and feel like they’re walking through the grass.”
For those ready to actually move in the real world, the company also has a product called EXOwalk. Here, an exoskeleton is strapped to the patient’s limbs and can help move their legs (again, in multiple modes). But this exoskeleton is fixed to a rolling robotic platform – meaning the patient actually moves forward on the ground, rather than being fixed to a static machine.
“This is driven – so they actually move along the hallway in the facility.”
EXO Motion
For patients with upper limb motor impairments, the company has developed a product called EXO motion. This is strictly a portable exoskeleton device that attaches to the arm. In active mode, it detects myolectric signals from the user’s arm and – with some sophisticated algorithms and mechatronics – converts those signals into mechanical motion that moves the arm.
In addition to these robotic devices, RpiO also is a leading company in software designed to help people with dementia.
“We have a high population of elderly people who suffer with this,” says Moh. “So the market is growing very fast.”
Below: CEO Jay Moh, followed by the R-BoT plus and display. Note the footprints…

INDRO’S TAKE
We enjoyed checking out these devices at Robot World 2023 – and were pleased to see yet more evidence of #robotsforgood.
“Robots can be tremendous tools on their own,” says InDro Robotics CEO Philip Reece. “But there’s something truly special about products designed to directly help human beings improve their mobility and health. We applaud the inventors and engineers who develop these products, and look forward to even more assistive device breakthroughs in future.”
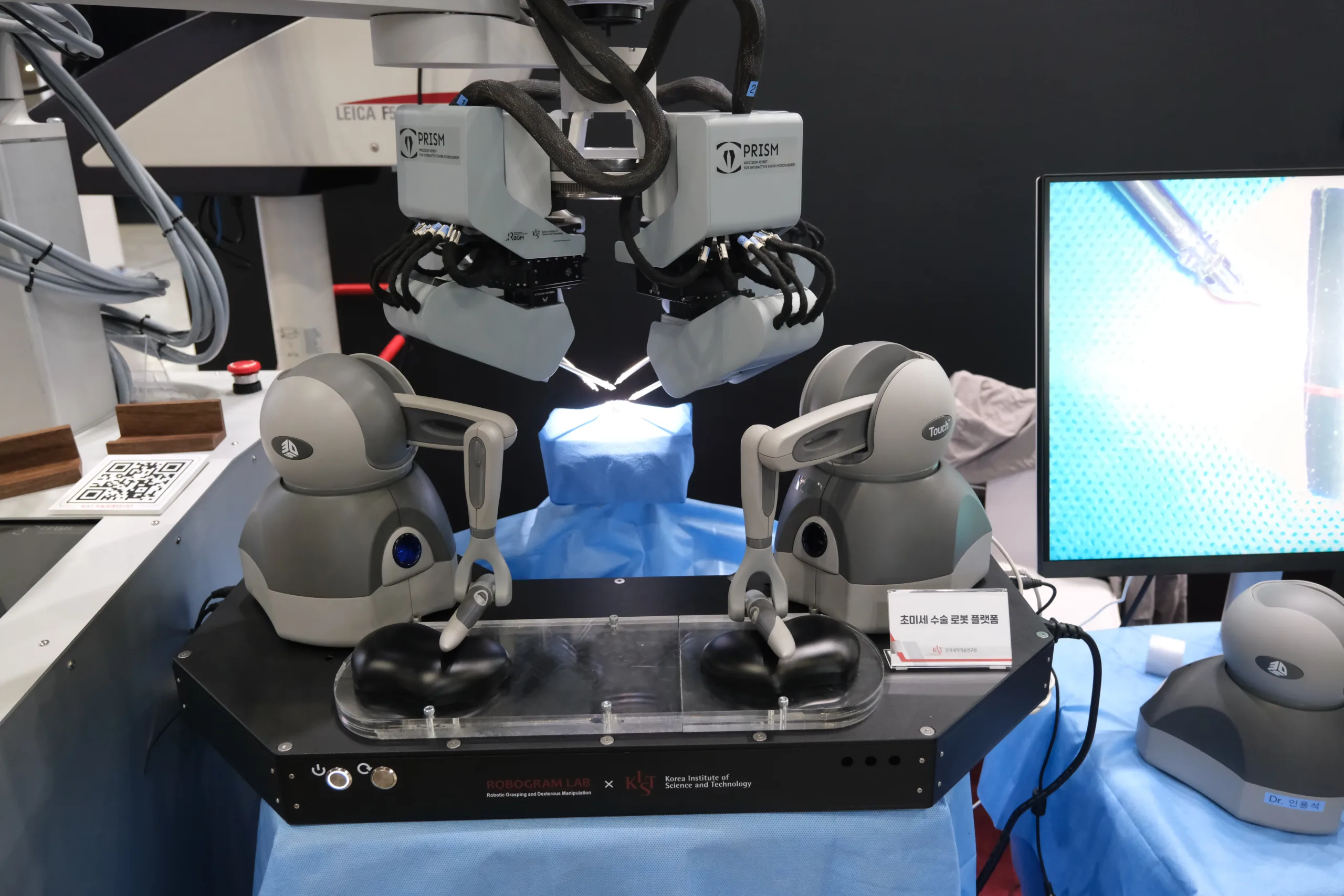
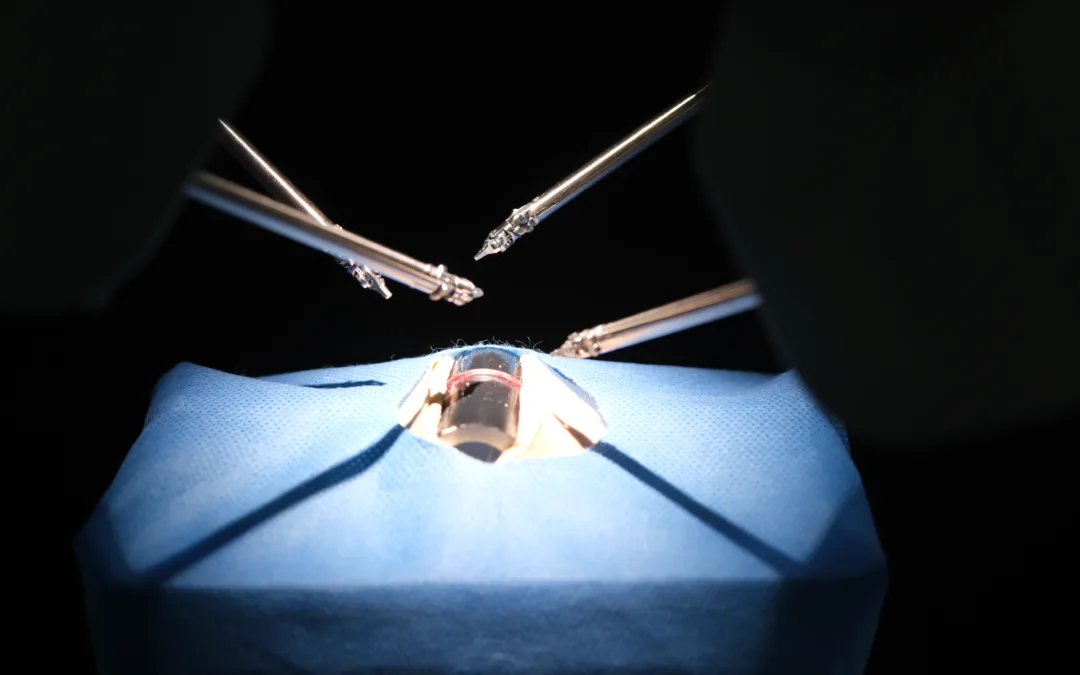
And a final note: The feature image at the top of this story shows some very, very, tiny arms used for microsurgery. InDro was able to take a run at the controls (pictured below). It took some patience, but we were able to grasp an impossibly small elastic band.
Now picture a highly skilled microsurgeon operating on someone remotely.
It’s happening now, thanks to robotics.