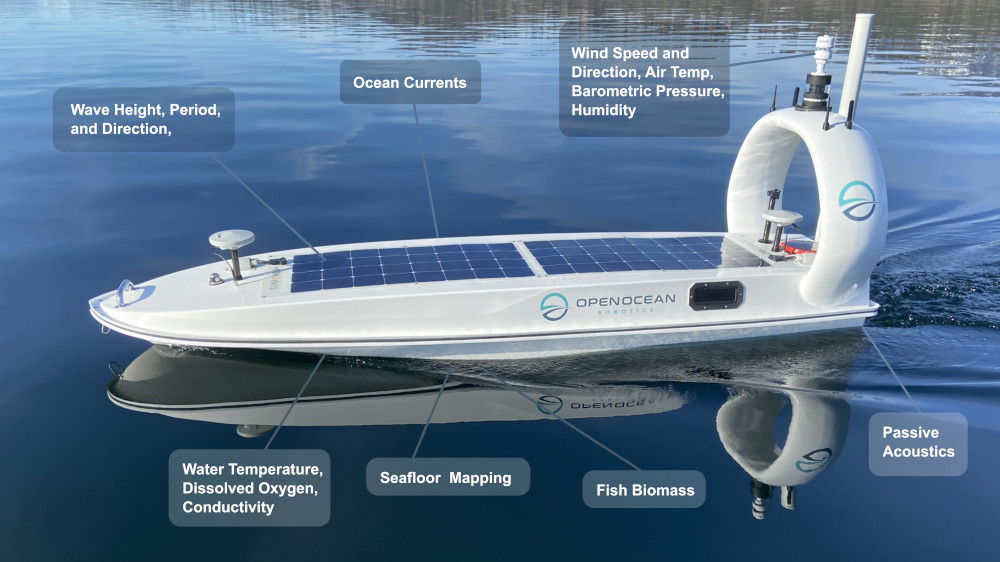
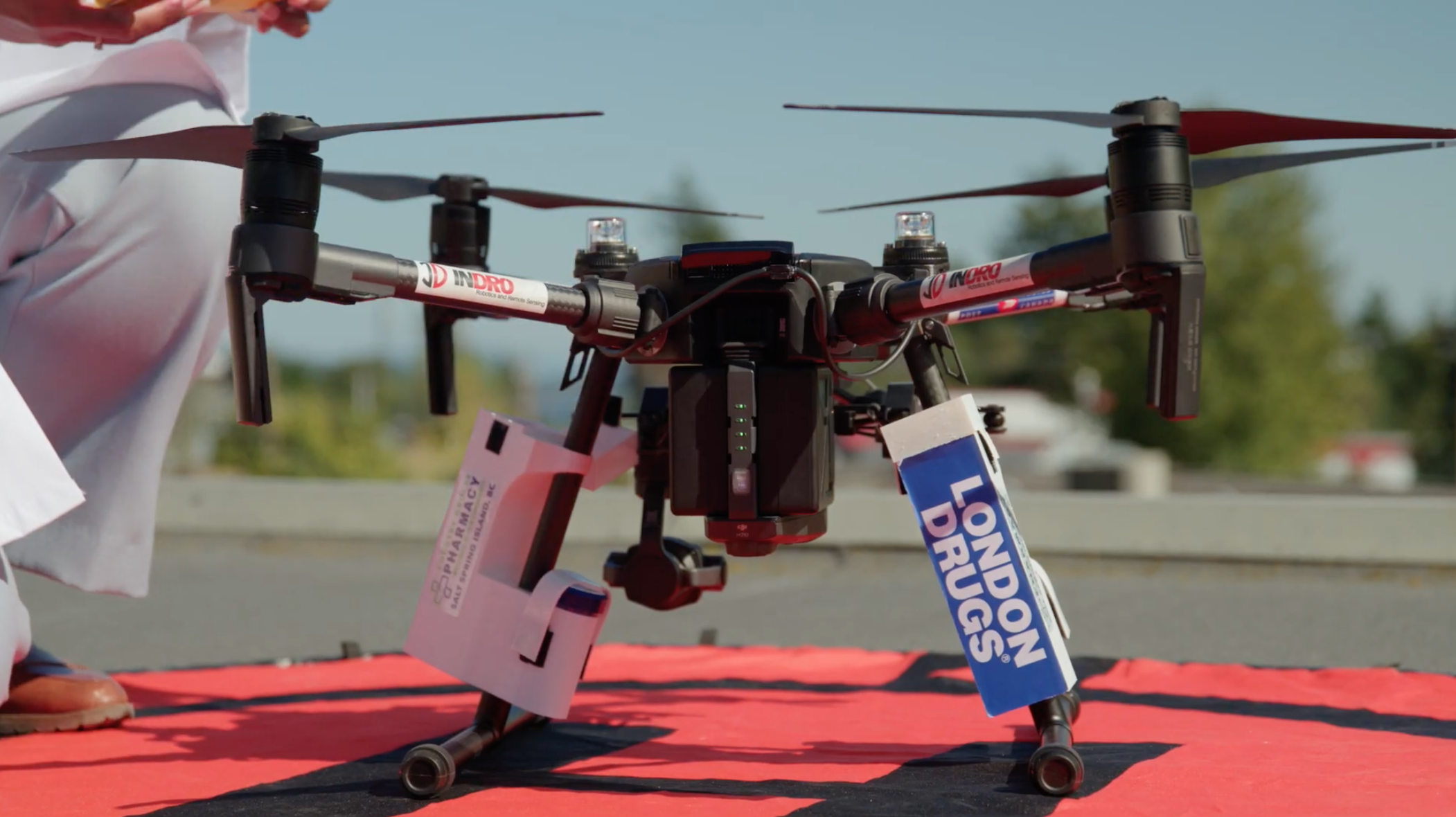
High-tech jobs aplenty in Ottawa – including with InDro Robotics
Ask someone what they know about Ottawa, and odds are they’ll say it’s home to the Federal Government, multiple world-class museums and the ByWard Market – a destination for locals and visitors alike.
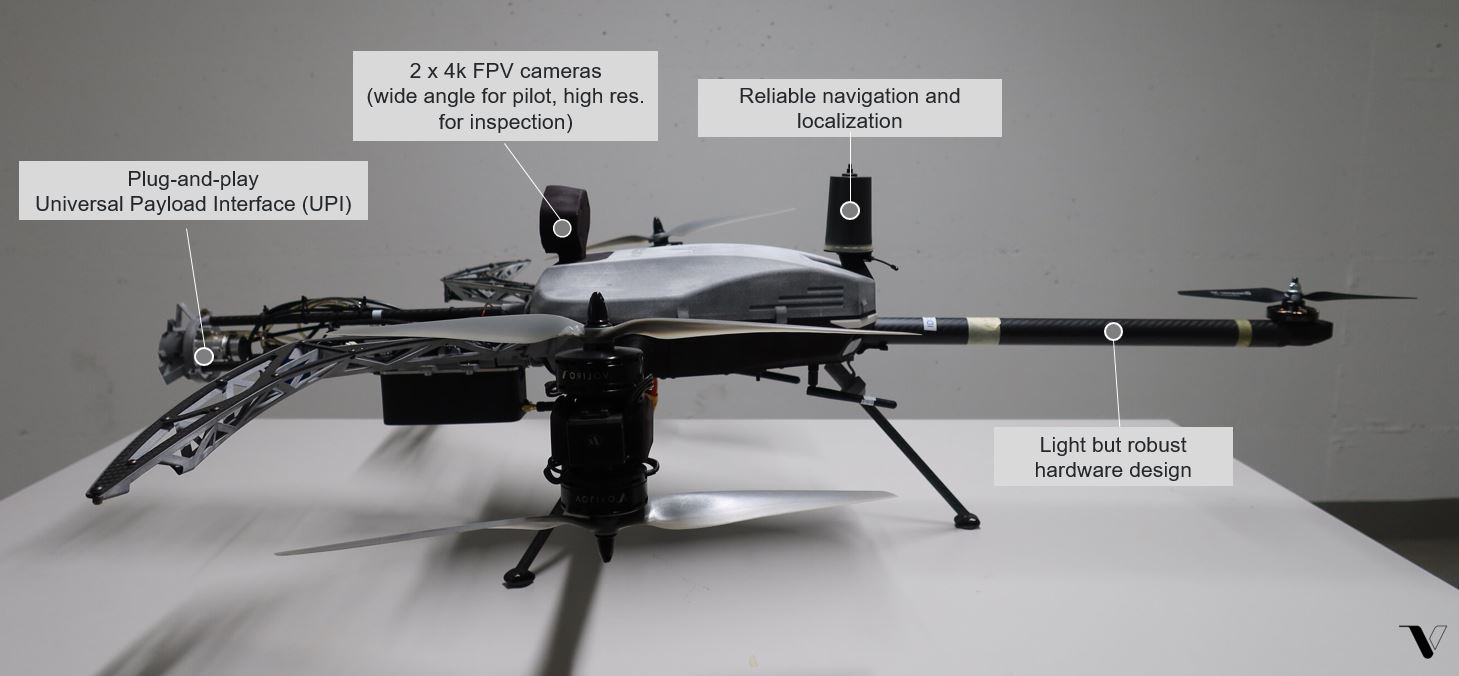
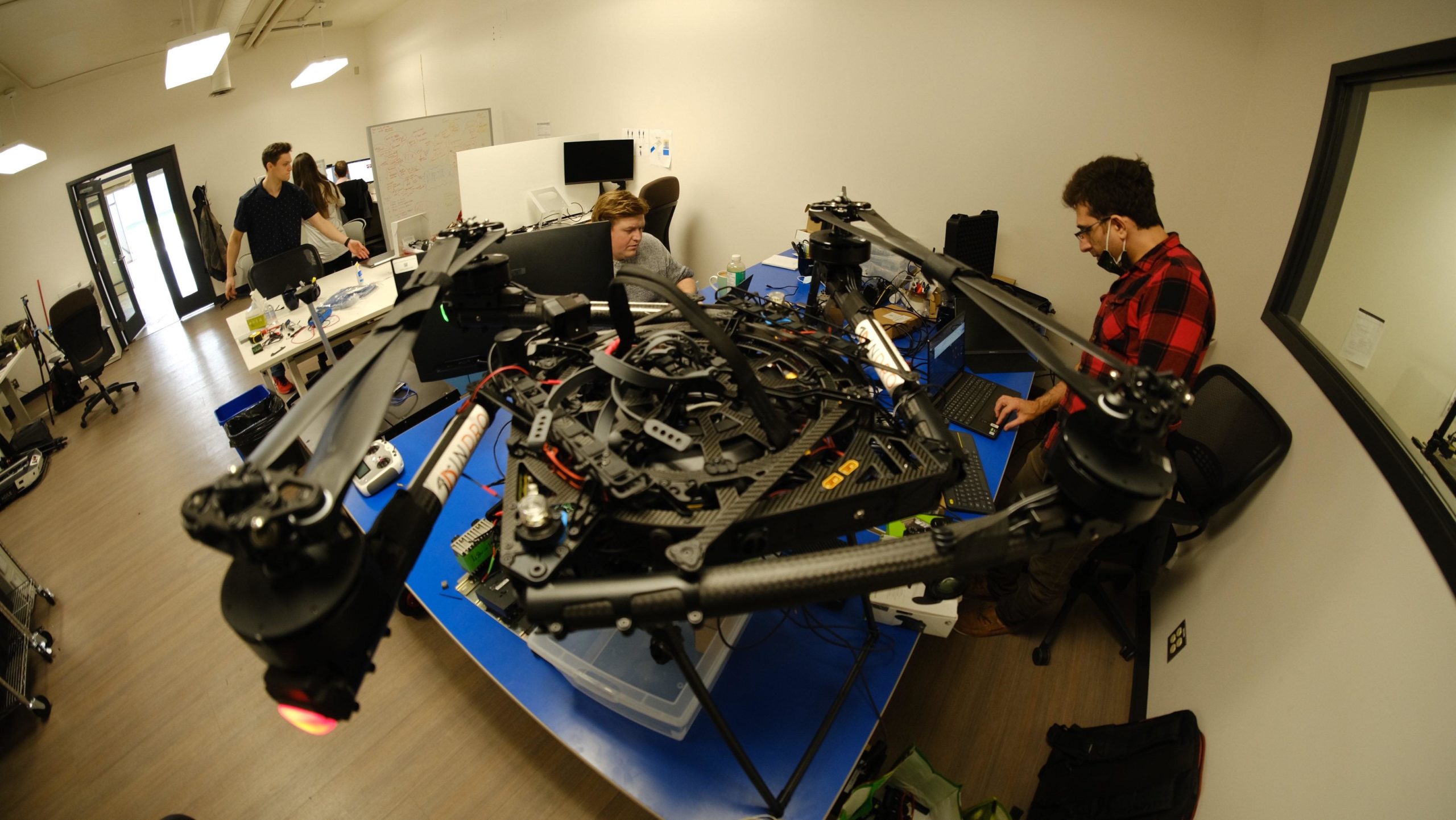
Increasingly, however, the nation’s capital is also becoming known as a high-tech hub. With facilities like the cutting-edge Area X.O – where robotic vehicles and drones are tested daily – Ottawa is becoming something of a technology magnet.
There’s data to back that up. Silicon Valley’s Gigamon recently announced plans to locate a new R&D facility in Ottawa, and the tech sector currently accounts for 11.3 per cent of all jobs in the city.
“When reviewing potential expansion opportunities in North America, we considered a number of attractive options,” Shane Buckley, president and CEO at Gigamon told Invest Ontario. “Ottawa’s diverse workforce and bustling tech community made it the clear choice.”
Taken together, it adds up to jobs.
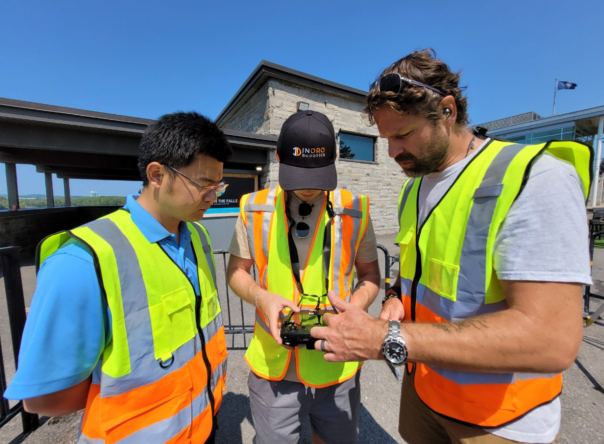
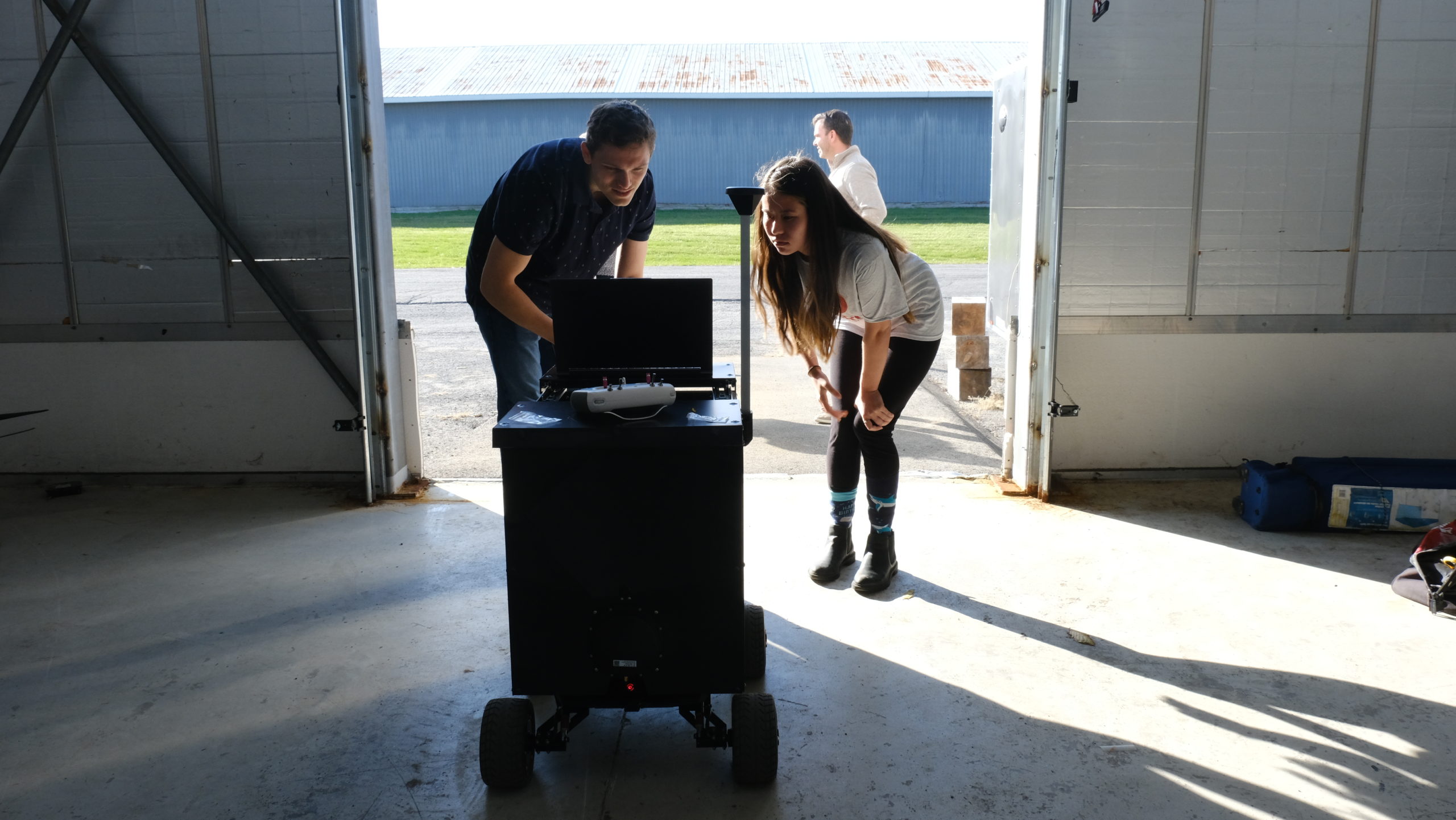
Below: InDro Robotics engineer Ahmad Tamimi solving problems at Area X.O

Job alert
A new blog post from Invest Ottawa highlights ten Ottawa high-tech companies that have current current job openings – with many of them advertising multiple openings.
Just one example? RideShark – a mobile app that offers multiple and seamless transportation options – has three positions open: Front-End Developer, Mobile App Developer and Business Development Sales Manager
Here’s more about what RideShark does:
Wait – there’s more!
In the Invest Ottawa blog about those jobs, there was also an opening highlighted at InDro Robotics. Here’s a screen grab from the blog, which offers some of the details.

InDro’s Take
Well, let’s be honest. We can’t help but be a little biased here.
InDro Robotics is a great place to work. We value team-playing, problem-solving people. Our engineers routinely work together on projects, and also alone – but always within a collaborative atmosphere. We have a diverse group of employees and our retention level is outstanding. Plus, working for InDro is fun: You might be flying a drone one day, or working on a ground robot the next. Trust us on this: No one gets bored.
We have multiple positions open at the moment, including some at our Area X.O location – and others in beautiful British Columbia.
Interested? You can check out the open positions on this page.