InDro Robotics and T-Mobile: A 5G match
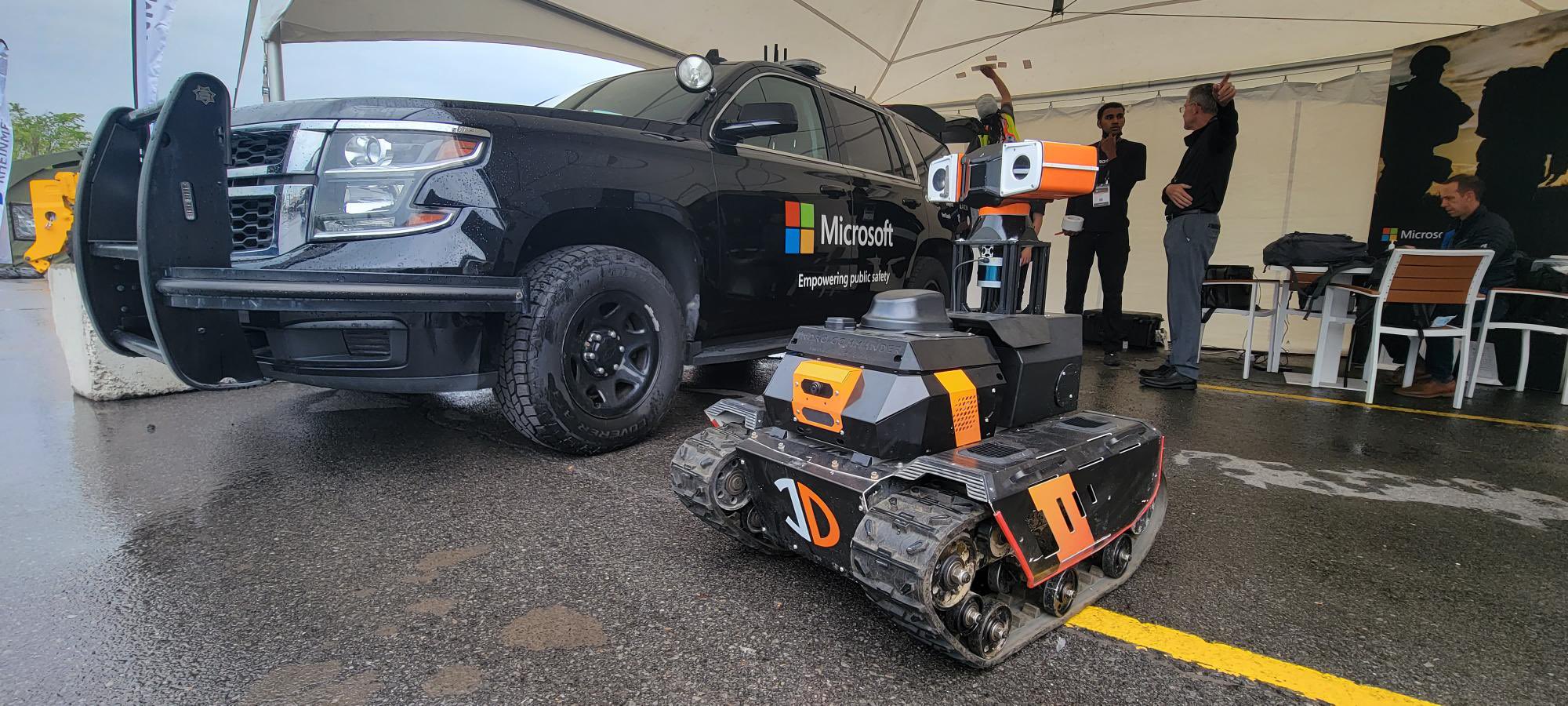
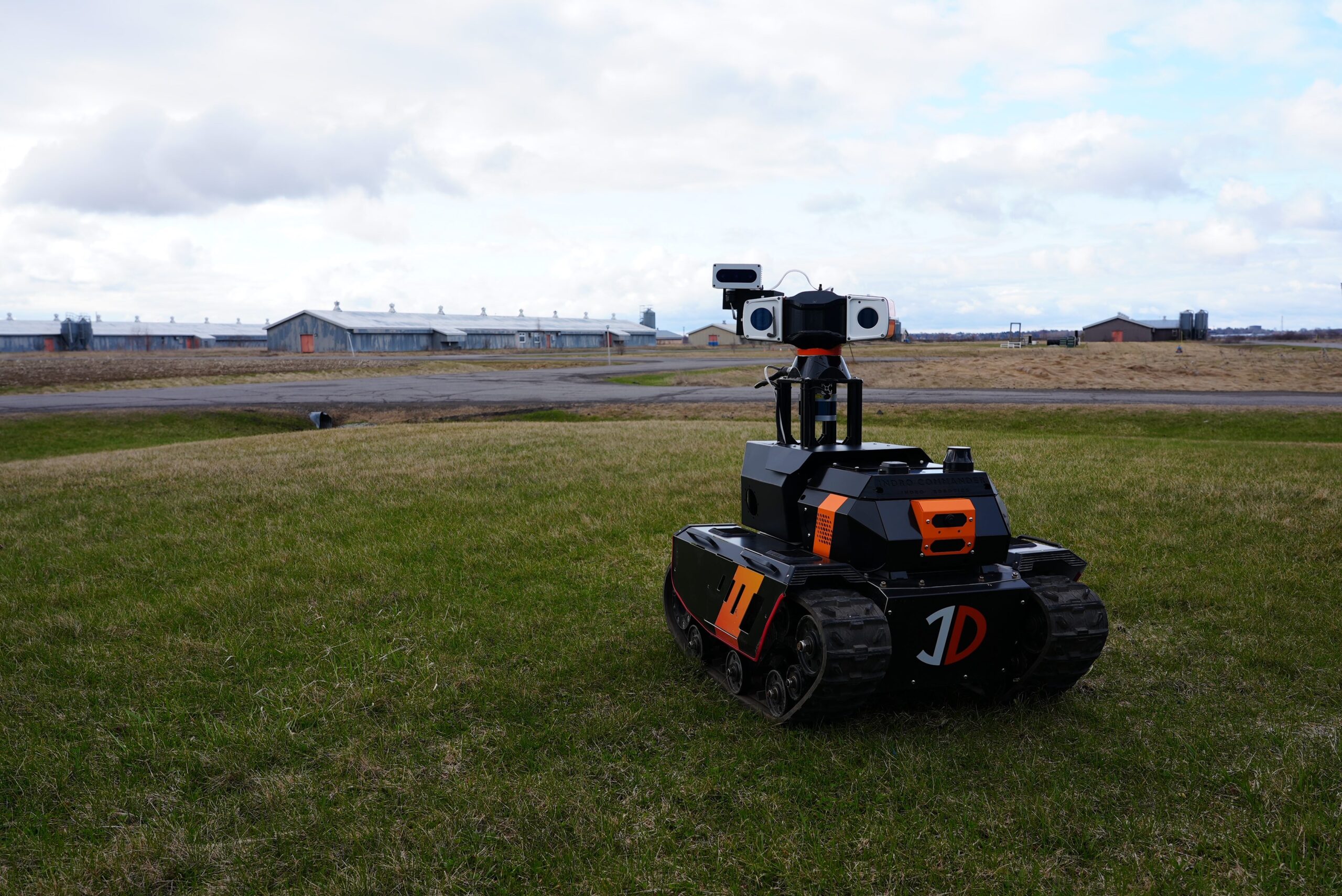
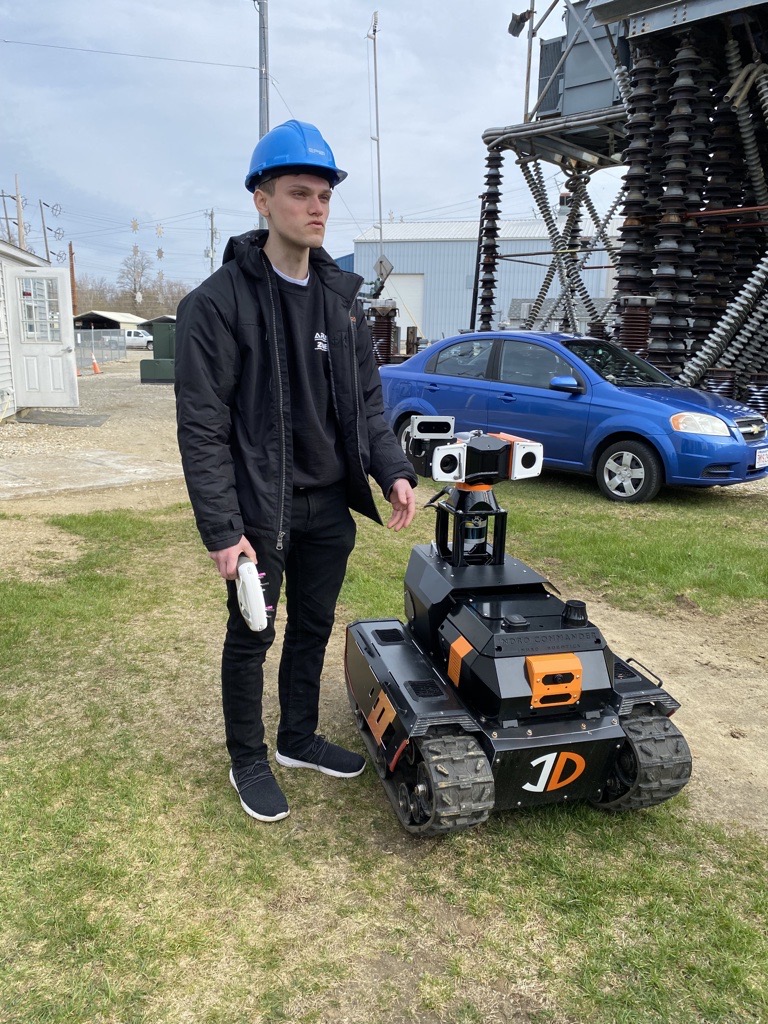
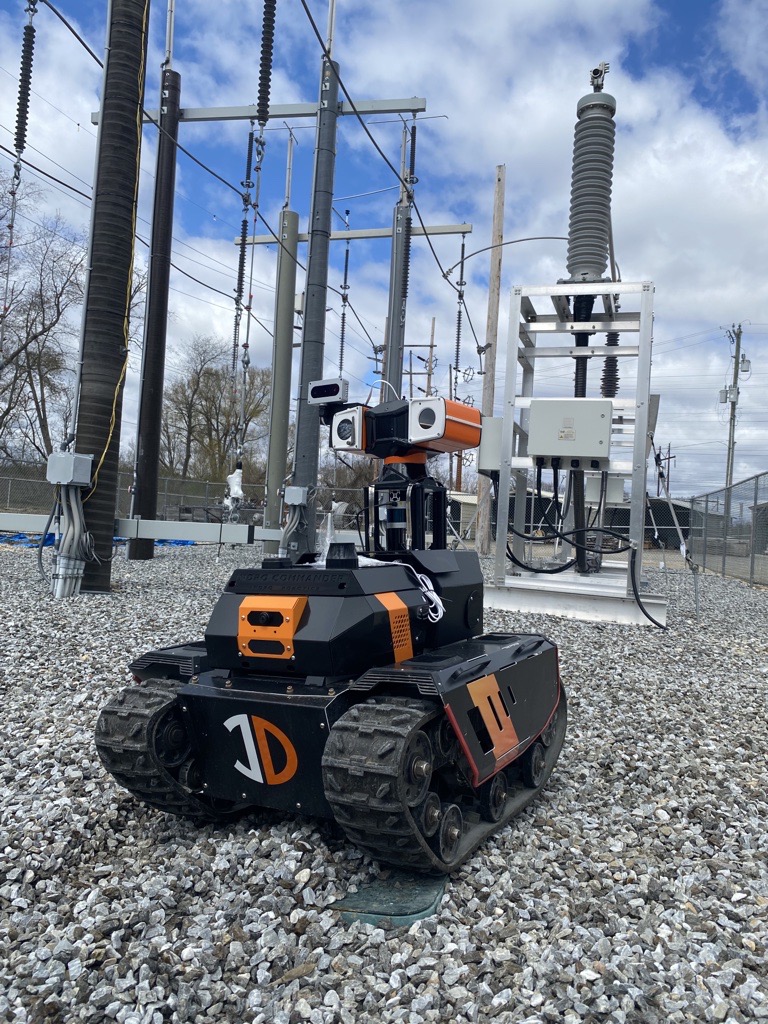
InDro Robotics was recently invited to attend an analyst’s summit in Bellevue, Washington State, put on by T-Mobile for Business. We were demonstrating remote operations of our Sentinel inspection robot, with Command & Control taking place over the 5G network. We were at the summit; the robot was in Ottawa.
We’ll get to that in a moment. But first, it’s worth looking at how InDro became involved with T-Mobile. It began with a different invitation. This one, from the Electric Power Research Institute, or EPRI.
EPRI is a major non-profit that does research and development to improve the efficiency of power generation and delivery. As the Institute states: “EPRI’s trusted experts collaborate with more than 450 companies in 45 countries, driving innovation to ensure the public has clean, safe, reliable, affordable, and equitable access to electricity across the globe.”
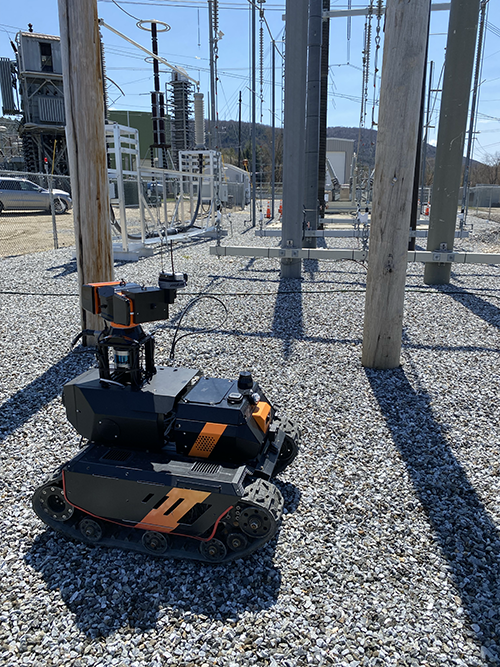
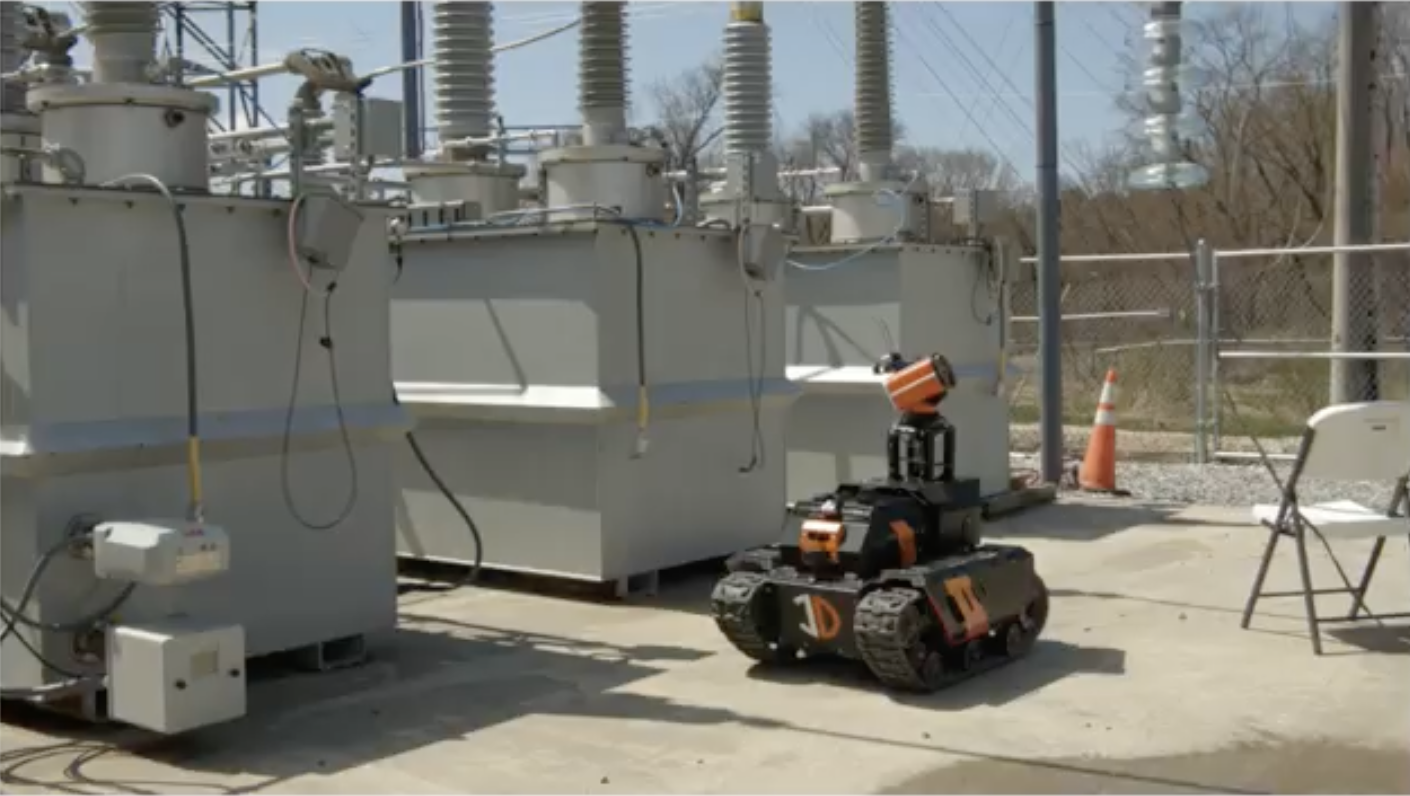
EPRI does a *lot* of testing within its R&D scope, often looking to find Best Practices it can share with its members. And in 2022, EPRI decided it wanted to put some ground robots to the test. Specifically, it was interested in how remotely operated or autonomous robots might be used to inspect electrical substations. These are usually remote, unstaffed facilities where high voltage is stepped down prior to being delivered to consumers (though some substations step up voltage).
EPRI invited a few ground robot manufacturers to its testing facility in Lenox, Massachusetts to see how well robots could carry out remote inspection. That facility is an electrical substation that can be energised or de-energised. It also features a set of overhead water pipes that can be used to simulate rain.
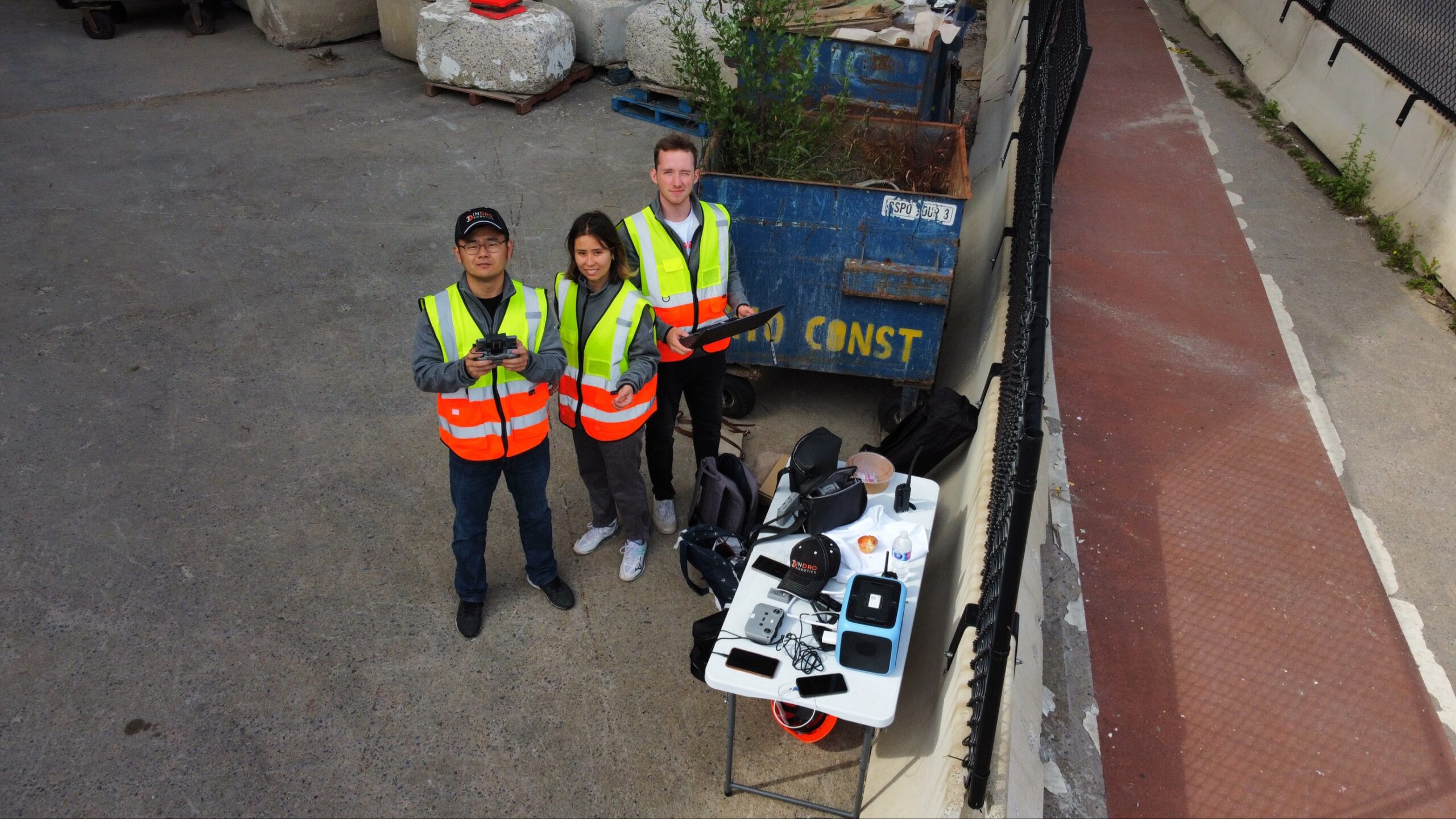
And so, earlier this year, InDro Robotics packed up Sentinel for the test.

The 5G connection
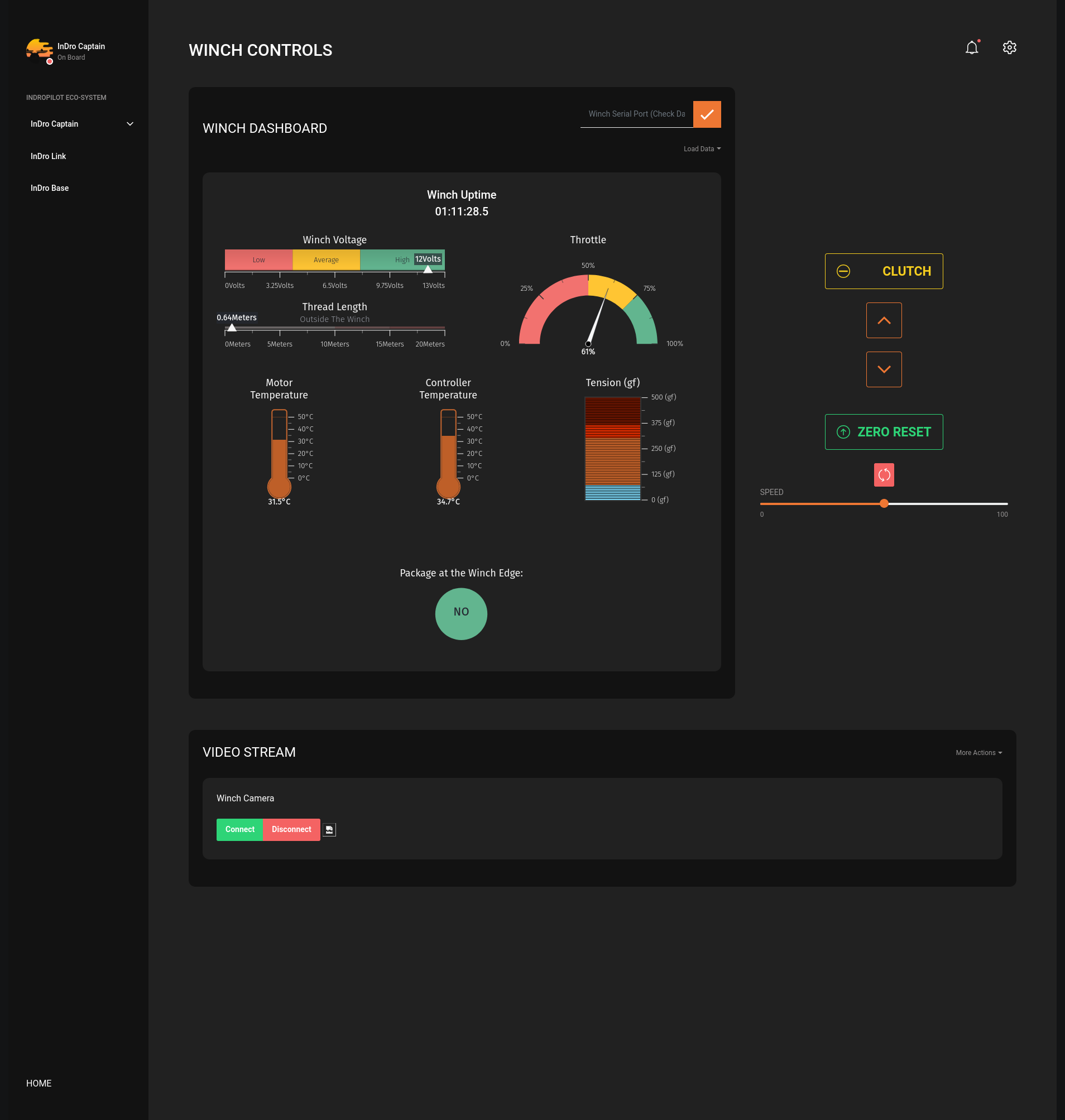
Sentinel, like all of our ground robots (and drones), has been modified by InDro to enable remote teleoperations. By connecting to 4G or 5G networks at both ends, InDro devices can be operated from hundreds and even thousands of kilometres away. But while 4G works for many operations, 5G is the gold standard.
That’s because 5G allows for dense data downloads, virtually in real-time. Since the Sentinel robot is equipped with multiple sensors (30x optical zoom pan-tilt-zoom camera, thermal, and sometimes LiDAR), a large data pipeline is advantageous. Not only does it enable real-time, minimal latency for the operator – it also allows for direct data uploads to the cloud.
InDro, of course, is based in Canada. And the EPRI test facility is based in the US. That meant we required a high-speed, robust cellular network in the US to carry out the test.
Because InDro is an R&D company, we did extensive research prior to selecting a US carrier. We wanted to make a single choice and stick with it, given the growing number of deployments in the US.
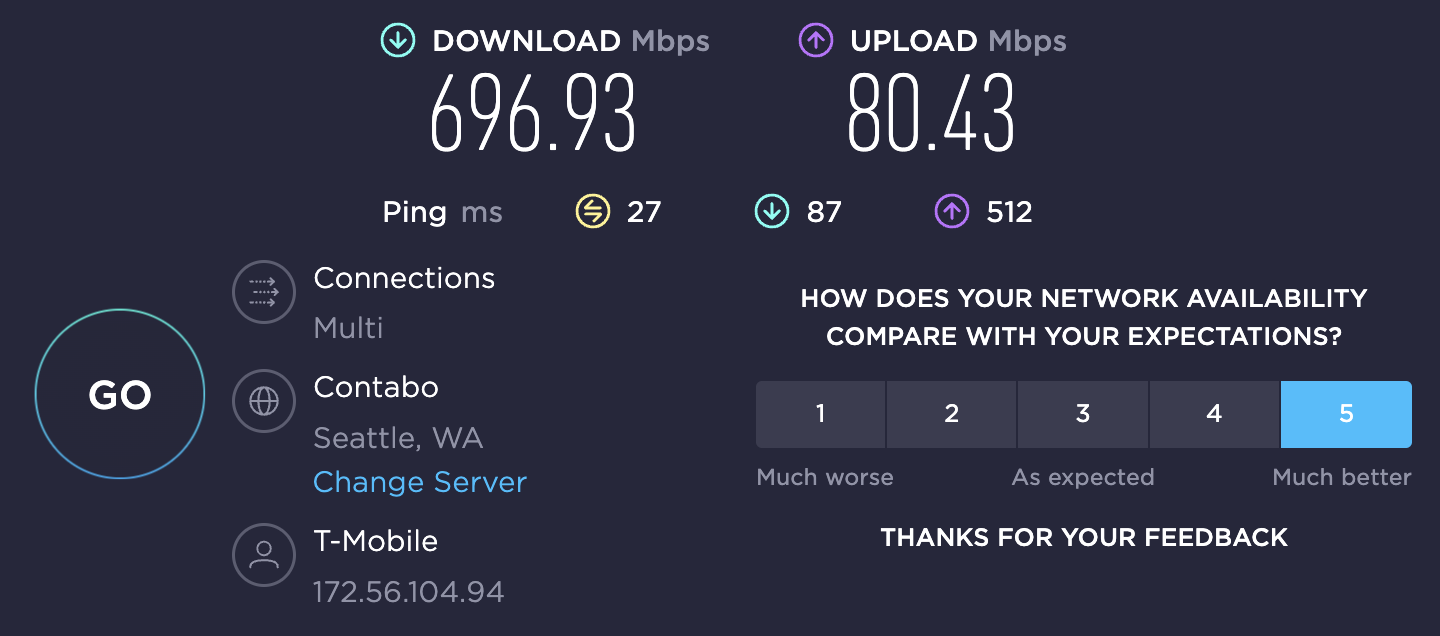
The choice quickly became obvious: T-Mobile. Its 5G network covers the entire country, with new towers being added each week. T‑Mobile has 5G speeds nearly twice as fast as its competitors. Typical download speeds on T‑Mobile’s 5G network are 75 – 335 Mbps with peaks over 1Gbps.
And when we were in Bellevue on T-Mobile’s network? Just check out the speed test below:
T-Mobile Summit
T-Mobile got wind of us selecting them as our network of choice for US operations. The company even issued a news release on that front. And Peter King, InDro’s Head of Robotic Solutions, wrote a guest blog about the Lenox experience and why a solid 5G network is so important to this kind of work.
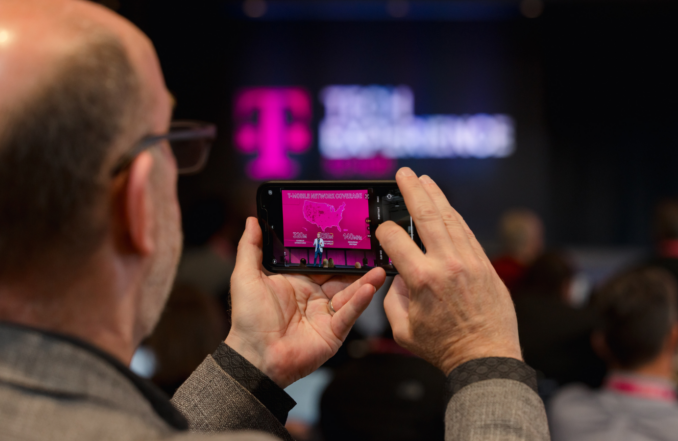
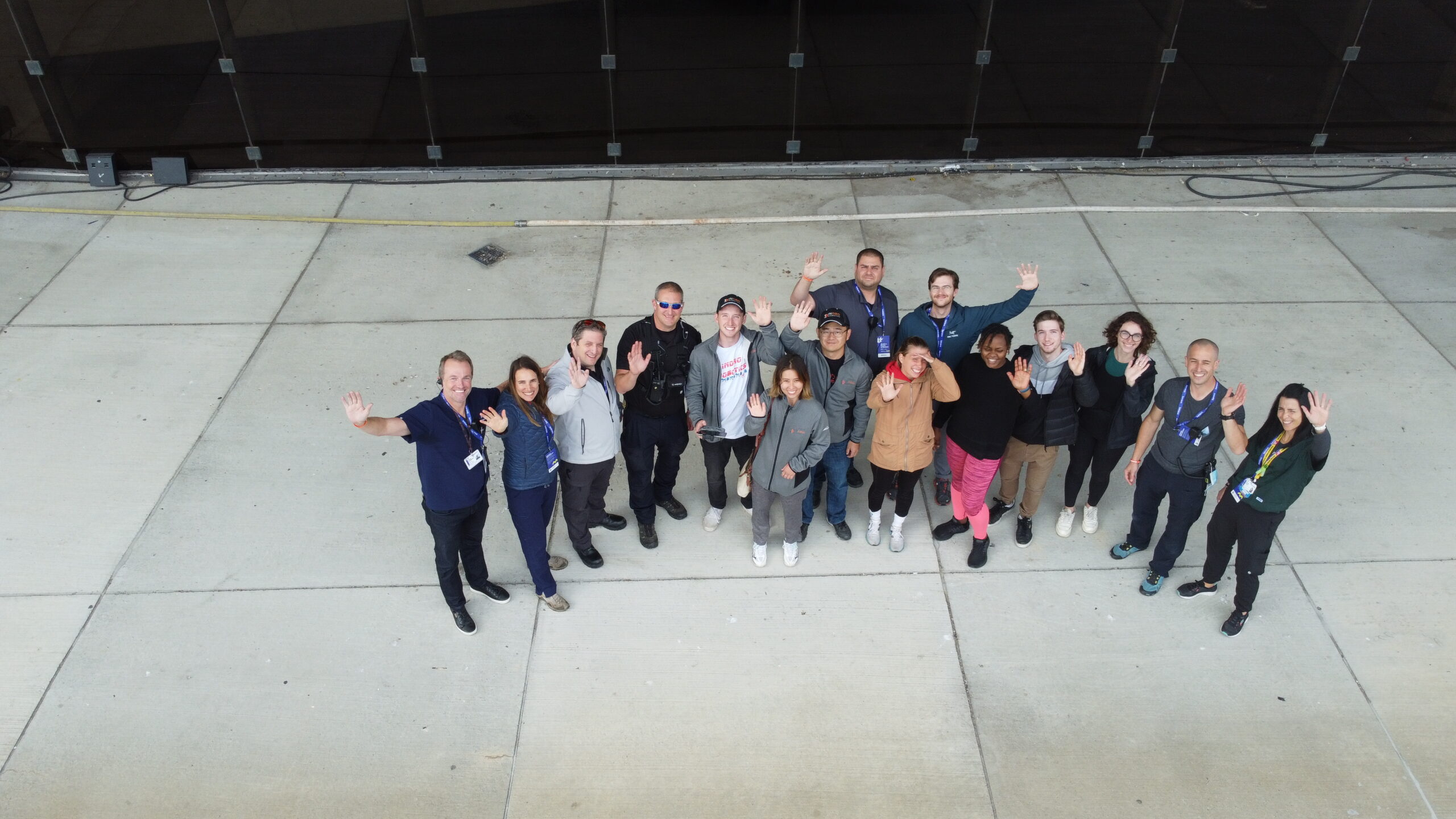
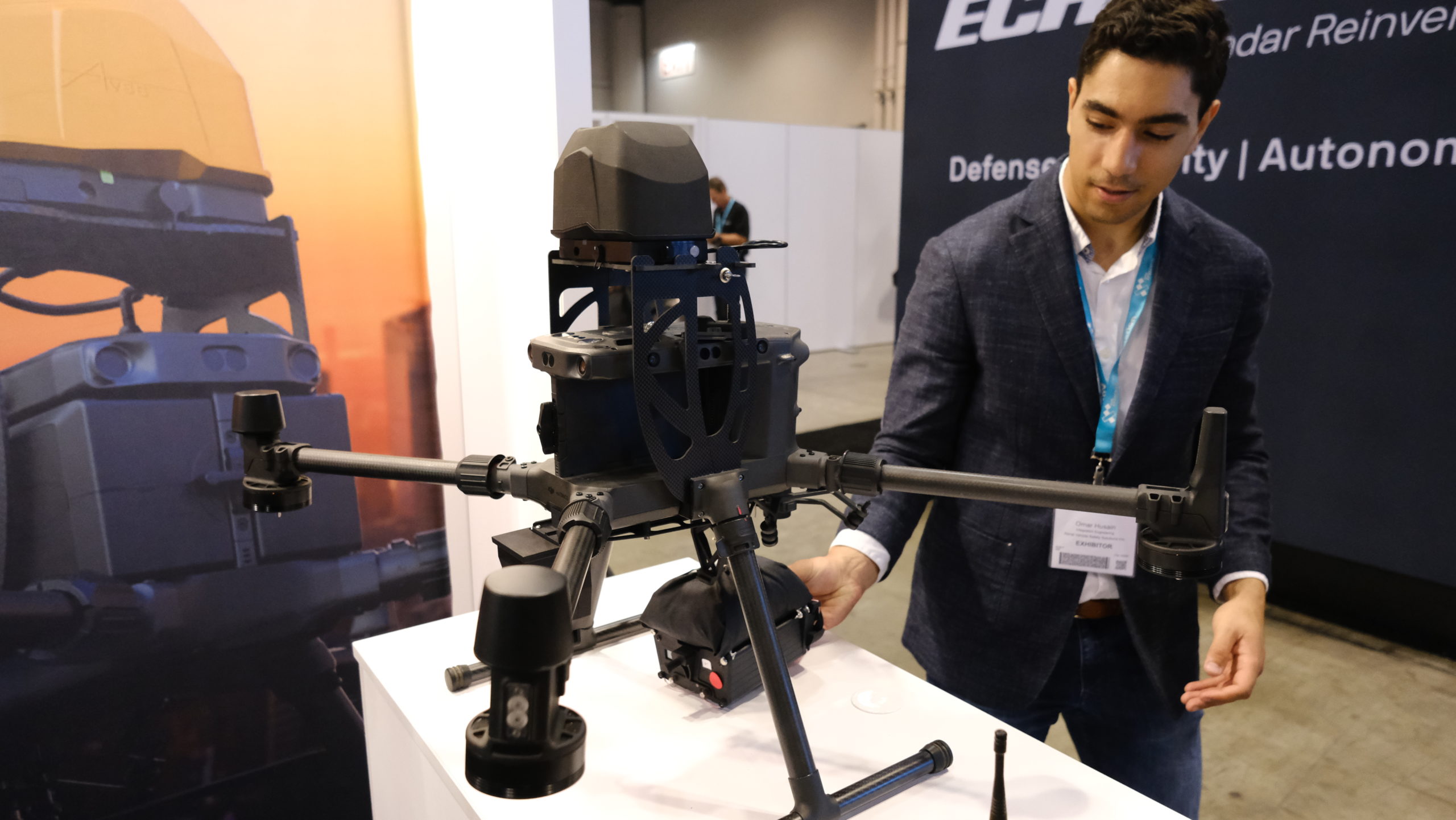
And all of that? Well, it led to InDro being invited to the first-ever T-Mobile for Business Analysts Summit, held in Bellevue in October. We were asked to demonstrate the low-latency and data throughput that 5G enables. And what better way than to have our Sentinel robot connected to 5G in Ottawa…with us connected to 5G in Bellevue.
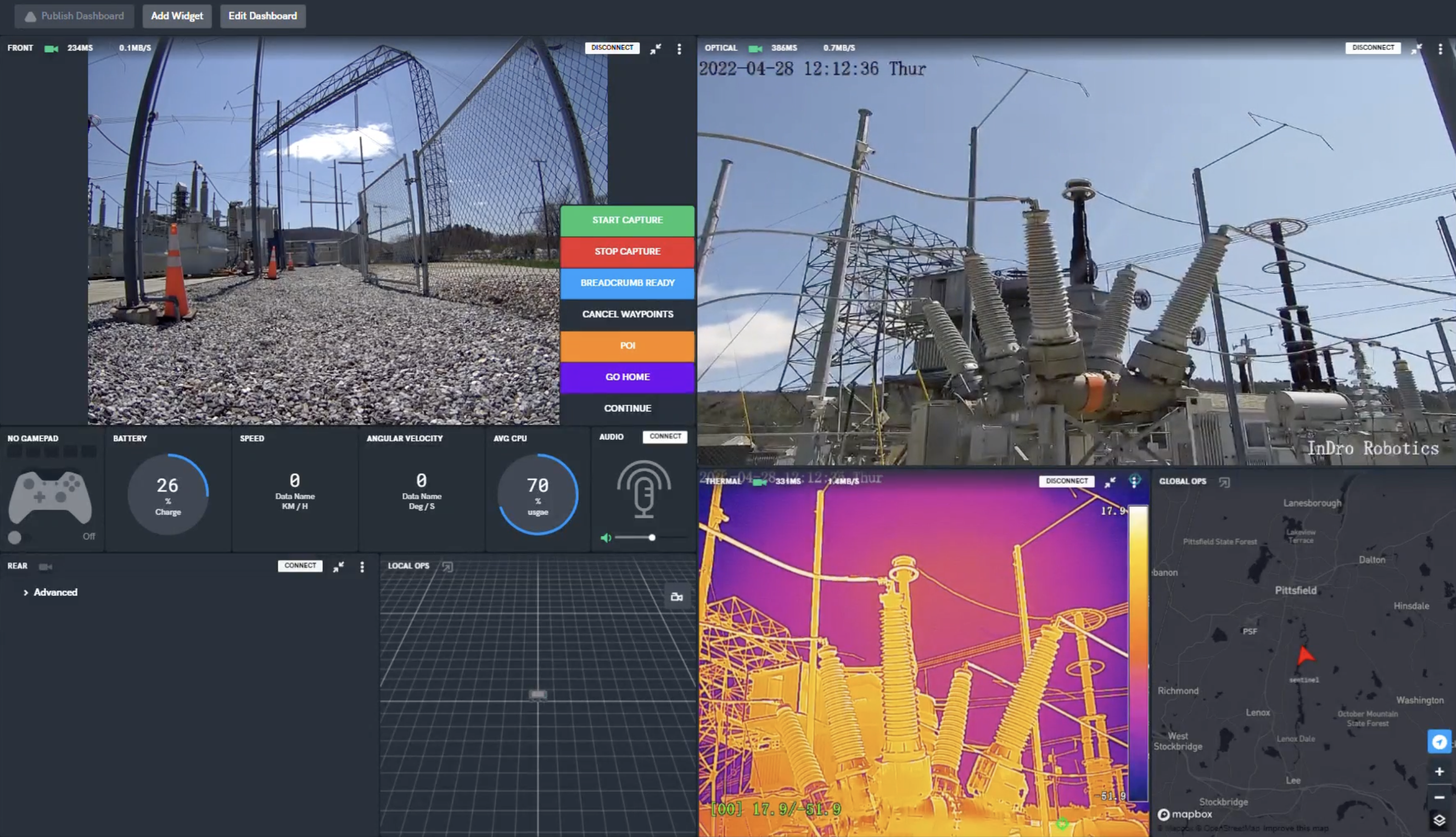
Those attending the summit were invited to the InDro display, where they could operate the robot using a simple Xbox controller. Video and thermal imaging were returned in real-time. But the real star of the show was near-zero latency. Seriously, the instant the controller was touched Sentinel would respond.
The hands-on demo even impressed John Saw, a McMaster engineering graduate who’s now the Executive Vice President, Advanced & Emerging Technologies at T-Mobile. Here’s John, controlling Sentinel over 5G in Ottawa from more than 4100km away:
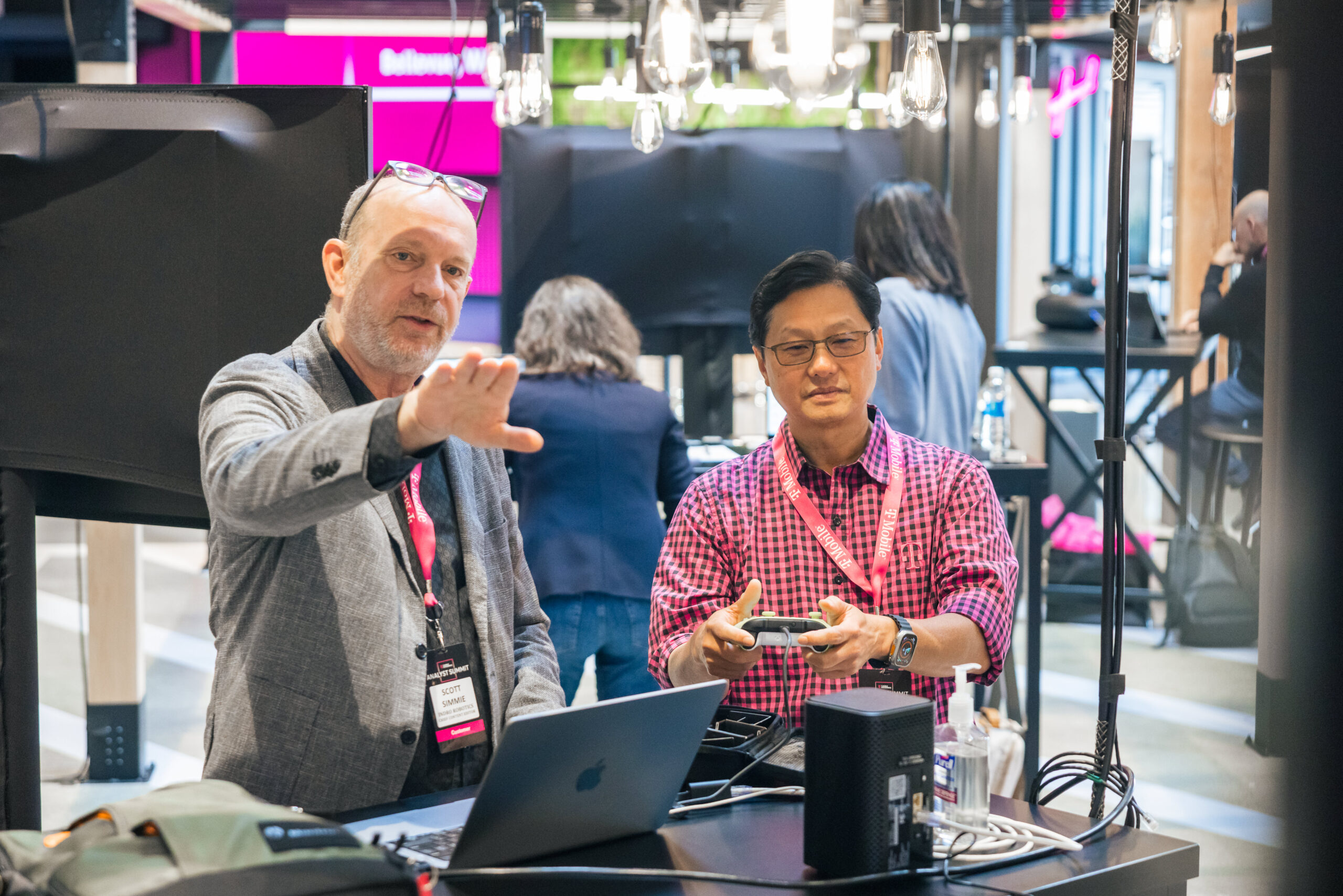

It’s clear John Saw thought the experience was kind of cool – and indicative of the kind of applications 5G unlocks.
In fact, he even mentioned it to the analysts:
InDro’s take
5G connectivity is about a lot more than phone calls. The speed and bandwidth of 5G is what will power the growing Internet of Things. And our Sentinel robot, arguably, is an IoT device. Operating it using T-Mobile’s network in the US, connected to the private 5G network at Area X.O, was a snap.
“Building ground and aerial robots that can be operated from great distances is integral to InDro Robotics and its clients,” explains InDro CEO Philip Reece. “But this capability can only be realized with fast, reliable networks. T-Mobile was the obvious choice for our US operations – and we look forward to many more deployments over 5G in the future.”
Finally, a shout-out to T-Mobile for Business. Thanks for inviting us to Washington State; it was a privilege to be able to showcase our technology with the help of your 5G network.