By Scott Simmie
A drone pilot has been hit with fines totalling more than $3,000 for two unauthorised and potentially dangerous flights at YOW – the Ottawa International Airport.
The flights took place in December of 2022 and involved the drone flying in close proximity to active runways while aircraft were landing. The flights were detected – and the pilot located – by the YOW Drone Detection Pilot Project. InDro Robotics supplies the core technology for that system, which has been in operation some 2-1/2 years.
In fact, the system allowed police to be directed to the location of the pilot while he was flying the drone from inside his car at a hotel parking lot.
“The individual was quite surprised that a police cruiser pulled up – and expressed ignorance about flying in the vicinity of the airport,” says Michael Beaudette, Vice President of Security, Emergency Management and Customer Transportation with the Ottawa International Airport Authority.
“He said he wasn’t aware he couldn’t fly there.”
He was about to be educated.
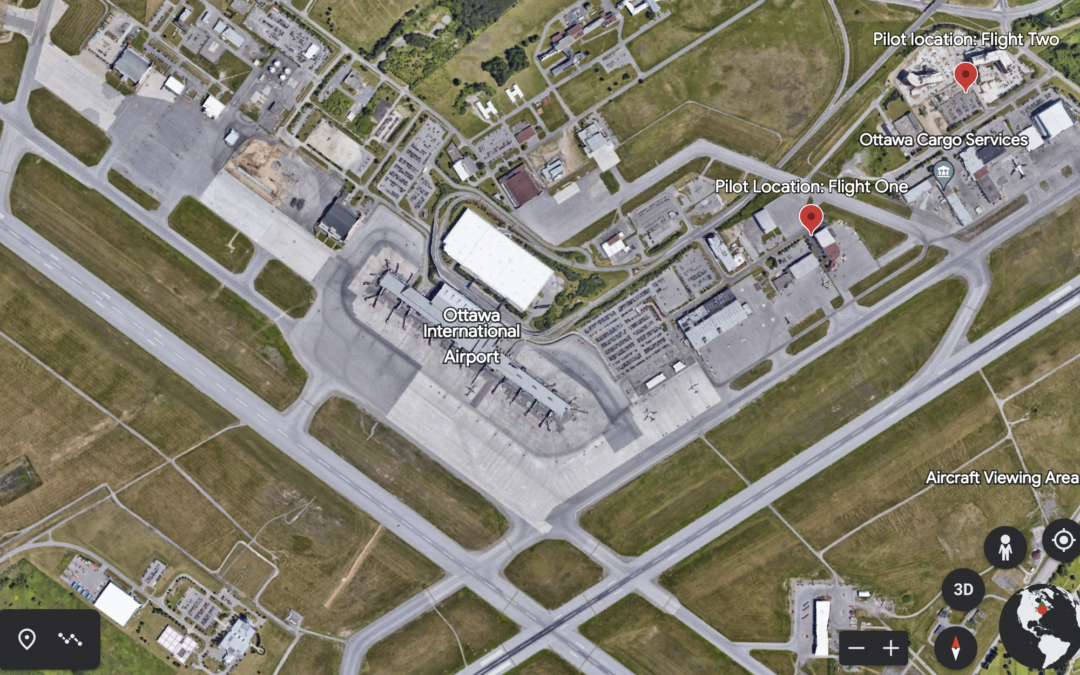
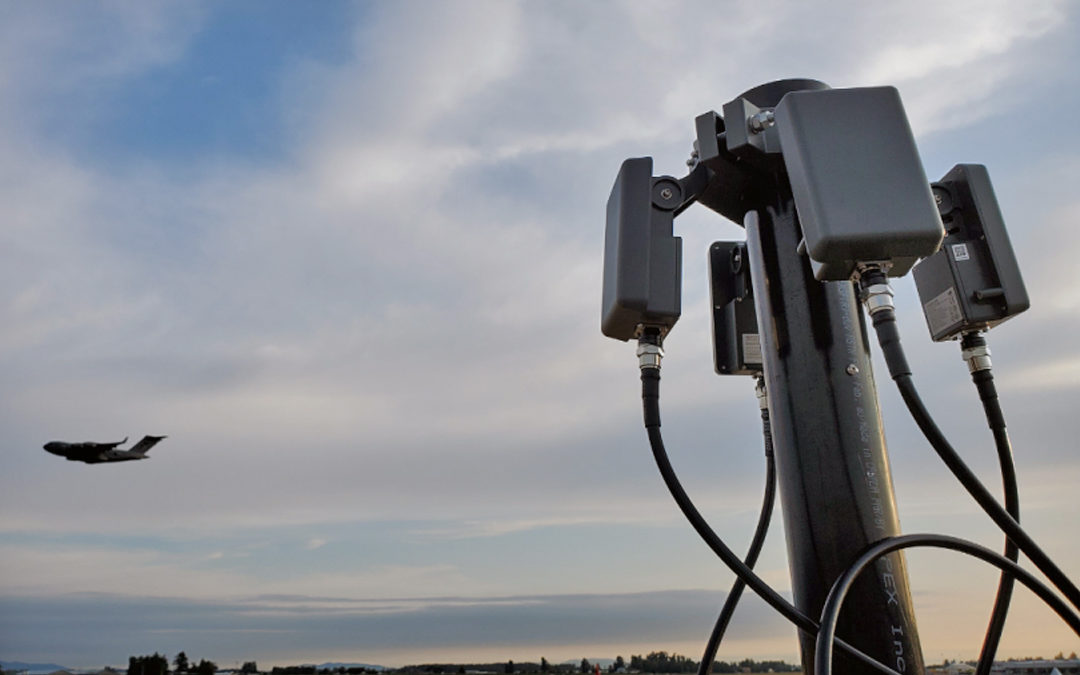
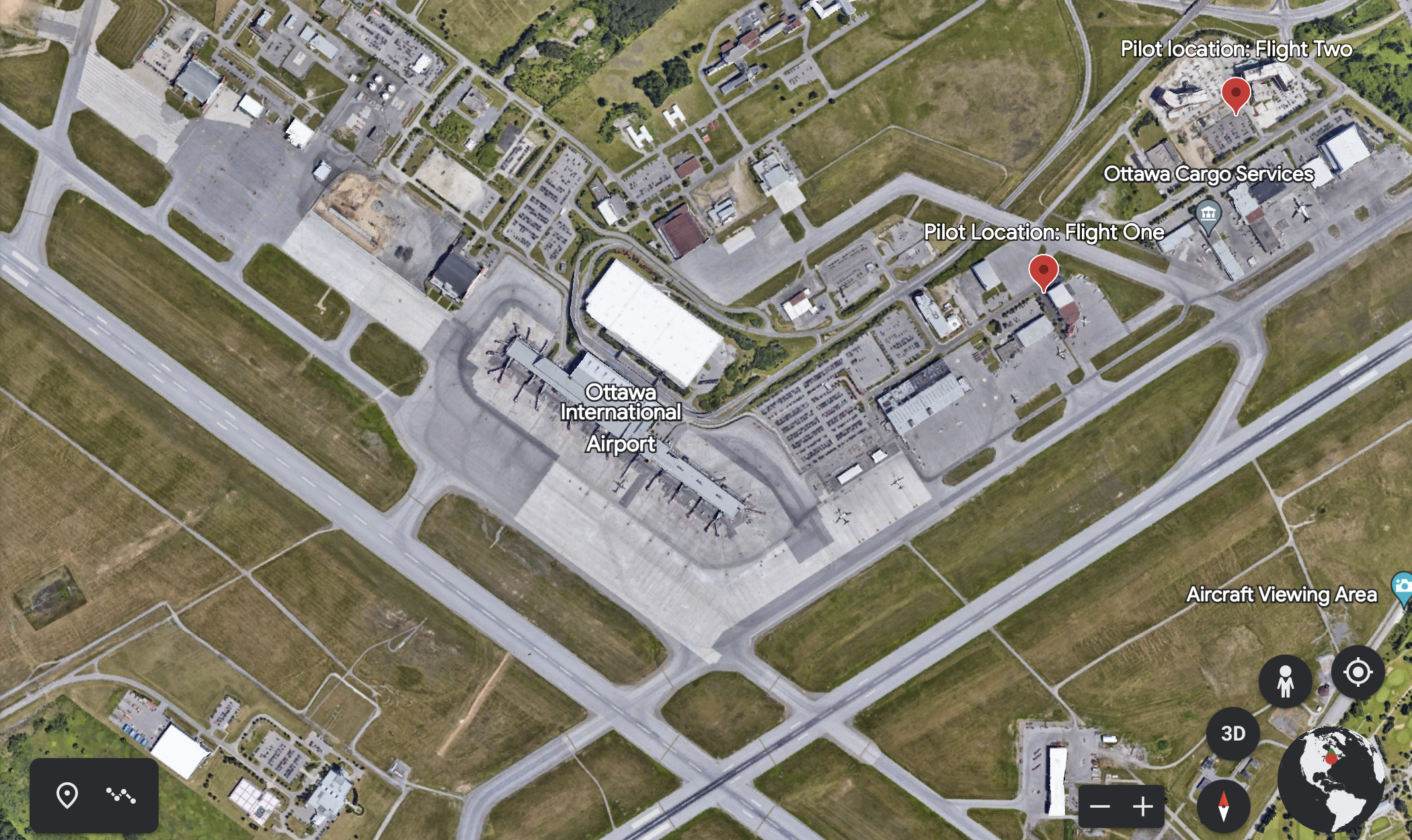
Below: Part of the YOW drone detection system, which uses multiple technologies

INTRUSION
The system at YOW is capable of detecting the location of active DJI drones up to 40 kilometres away. It is also designed to pick up on other brands of commercial drones flying at closer proximity to the airport by identifying their unique radio frequency signatures.
On December 20, the system generated an alert. Someone was flying a DJI Air 2S drone, which weighs 595 grams, adjacent to the airport.
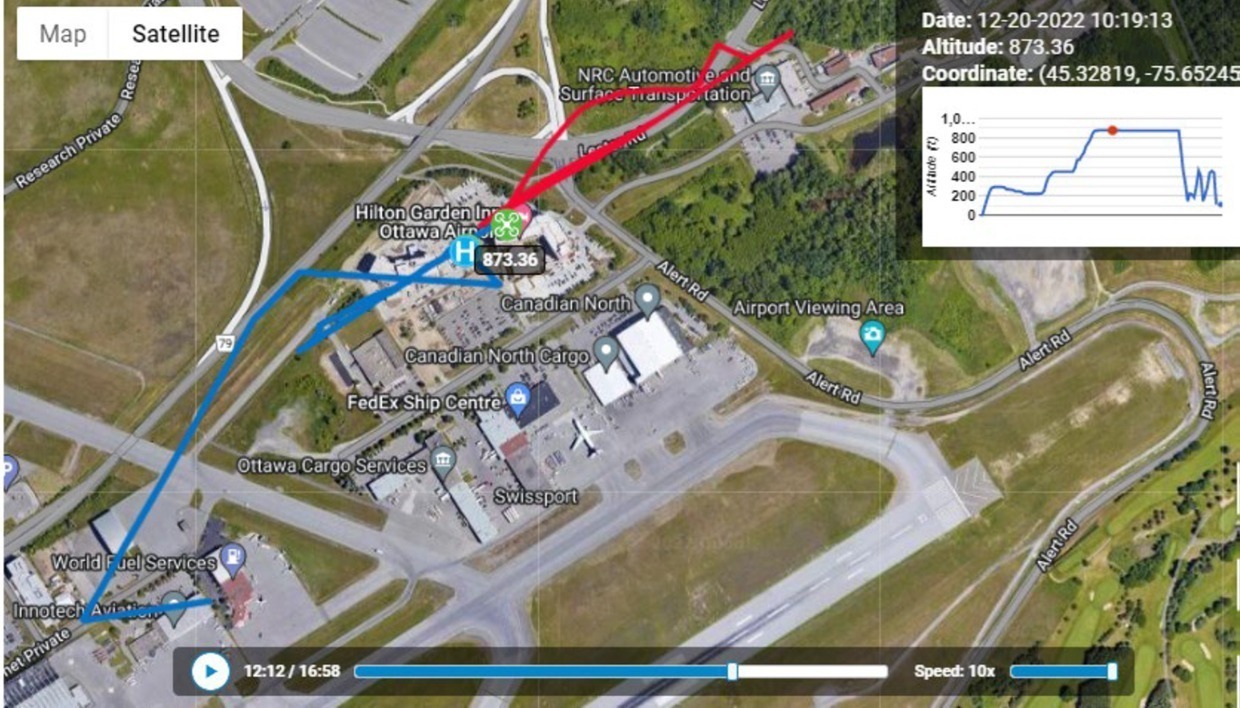
Flight one: The flight began at 10:07 AM and the drone and pilot were detected at the parking lot of the World Fuel Services building. The drone remained at ground level for five minutes; at 10:12 the operator and drone were detected near the hotel immediately adjacent to the airport – a likely indicator the pilot was in a vehicle and on the move. The drone began increasing in altitude, reaching a height of 873′ – nearly 500′ above the altitude allowed by Transport Canada in areas where drones are permitted. The flight lasted nearly 17 minutes, during which a helicopter arrived at the airport.
“Our Airport Operations Coordination Centre (AOCC) quickly checked to see if there had been any approvals granted for drone activity in the immediate vicinity of the airport and confirmed that there were none,” explains Beaudette. “They then notified the Airport Section of the Ottawa Police Service of the detection, who were then dispatched to the general area where the drone had been active. However, by that time the flight had been terminated.”
“When we received an alert of the second flight, we were able to track the drone flight in real time and pinpoint the exact location of the pilot,” adds Beaudette. “The Ottawa Police Service cruiser approached the pilot as he was sitting in his car piloting the drone and ordered him to land it immediately.”
It’s no surprise these flights were of great concern to authorities at the airport.
“Both flights took place without prior notification to, or approval by, NAV Canada,” says Beaudette. “The drone was operating within 350 meters of an active runway and during the first flight, the drone was also operating in very close proximity to a helicopter that was manoeuvering in the area.”
KNOW THE REGS
As the saying goes, “Ignorance is no excuse for the law.” In other words, being unaware of regulations provides zero legal cover. Police took the pilot’s information, which was passed along to Transport Canada.
That’s because it’s TC, not local law enforcement (with the exception of local bylaw infractions), responsible for enforcing rules that govern drones. And in Canada, those rules are found in Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARS), Part IX. (If you’re a drone pilot and haven’t read these yet, we highly recommend you do.)
THE PENALTIES
The pilot violated multiple sections of CARS. And each of those comes with a financial penalty. Here are the sections violated, and the fines assessed:
- CAR 900.06 – No person shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft system in such a reckless or negligent manner as to endanger or be likely to endanger aviation safety or the safety of any person. (Penalty assessed: $370.50)
- CAR 901.02 No person shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft system unless the remotely piloted aircraft is registered in accordance with this Division. (Penalty assessed: $370.50)
- CAR 901.14(1) Subject to subsection 901.71(1), no pilot shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft in controlled airspace. (Penalty assessed: $456.00)
- CAR 901.25(1) Subject to subsection (2), no pilot shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft at an altitude greater than (a) 400 feet (122 m) AGL; or (b) 100 feet (30 m) above any building or structure, if the aircraft is being operated at a distance of less than 200 feet (61 m), measured horizontally, from the building or structure. (Penalty assessed: $456.00)
- CAR 901.27 No pilot shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft system unless, before commencing operations, they determine that the site for take-off, launch, landing or recovery is suitable for the proposed operation by conducting a site survey that takes into account the following factors:
(a) the boundaries of the area of operation;
(b) the type of airspace and the applicable regulatory requirements;
(c) the altitudes and routes to be used on the approach to and departure from the area of operation;
(d) the proximity of manned aircraft operations;
(e) the proximity of aerodromes, airports and heliports;
(f) the location and height of obstacles, including wires, masts, buildings, cell phone towers and wind turbines;
(g) the predominant weather and environmental conditions for the area of operation; and
(h) the horizontal distances from persons not involved in the operation. (Penalty assessed: $456.00)
-
CAR 901.47(2) Subject to section 901.73, no pilot shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft at a distance of less than
(a) three nautical miles from the centre of an airport; and
(b) one nautical mile from the centre of a heliport. (Penalty assessed: $456.00)
-
CAR 901.54(1) Subject to subsection (2), no person shall operate a remotely piloted aircraft system under this Division unless the person
(a) is at least 14 years of age; and
(b) holds either
(i) a pilot certificate — small remotely piloted aircraft (VLOS) — basic operations issued under section 901.55; or
(ii) a pilot certificate — small remotely piloted aircraft (VLOS) — advanced operations issued under section 901.64. (Penalty assessed: $456.00)
Add that all up? It comes to $3021.00. Those are pretty significant consequences for the pilot.
Below: The blue and red lines indicate the drone’s path; you can see at the top right the maximum altitude was more nearly 900′ AGL, and the drone was at that height for roughly a third of its time in the air.
A CAUTIONARY TALE
YOW was pleased to see that Transport Canada took this incident seriously. And Michael Beaudette hopes this incident can be used to raise awareness.
“Firstly, to remind drone operators that Transport Canada has regulations regarding drones operating near airports and aerodromes to ensure the safety of the public both in the air and on the ground,” he says. “Secondly, that individuals who are not aware of, or do not respect these regulations can be detected and held accountable, as in this case, subjected to fines that could be in the thousands of dollars.”
Of course, these flights would likely have gone undetected were it not for YOW’s Drone Detection Pilot Project. This ongoing project, you may be aware, recorded multiple illegal flights during the so-called “Freedom Convoy” protests in Ottawa, and was put to use during US President Joe Biden’s 2023 state visit.
“It has opened our eyes as to how many drones are active in the National Capital Region, particularly, in and around our approach paths of our runways and in the immediate vicinity of the airport itself,” says Beaudette.
“It has also led to collaborative efforts between Transport Canada, NAV Canada and multiple Class 1 airports to become better aware of this issue and to develop contingencies to respond to incidents such as the one we experienced in Dec 2022.”
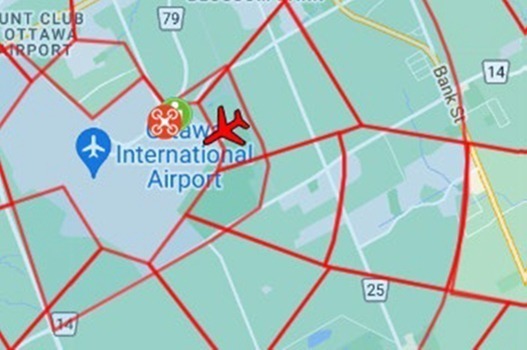
Below: Data showed the drone in the air as a crewed aircraft came in to land:
INDRO’S TAKE
InDro Robotics, like other Canadian professional operators, has a healthy respect for the CARS regulations. They are there for a reason, and not following the regs can lead to serious consequences. In fact, we wrote at length about a collision between an York Regional Police drone and a Cessna at the Buttonville Airport.
“There can be no question that drones flying near active runways poses a significant – and completely avoidable – threat,” says InDro Robotics CEO Philip Reece, who is also a licensed private pilot.
“The regulations are there for a reason: To protect the safety of crewed aircraft, as well as people and property on the ground. InDro is proud to be the core technology partner of the YOW Drone Detection Pilot Project – and this incident is a perfect reason why.”
Interested in a drone detection system? InDro would be happy to discuss your needs and offer our expertise. Contact us here.